글로벌 연구동향
방사선생물학
![[Biosci Rep. ] Digoxin enhances radiation response in radioresistant A549 cells by reducing protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A).](/enewspaper/upimages/admin_20171113161404_R.jpg) [Biosci Rep. ] Digoxin enhances radiation response in radioresistant A549 cells by reducing protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A).
[Biosci Rep. ] Digoxin enhances radiation response in radioresistant A549 cells by reducing protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A).KIRAMS/ 이지영, 정연경*
- 출처
- Biosci Rep.
- 등재일
- 2017 Oct 25
- 저널이슈번호
- pii: BSR20171257. doi: 10.1042/BSR20171257. [Epub ahead of print]
- 내용
Abstract
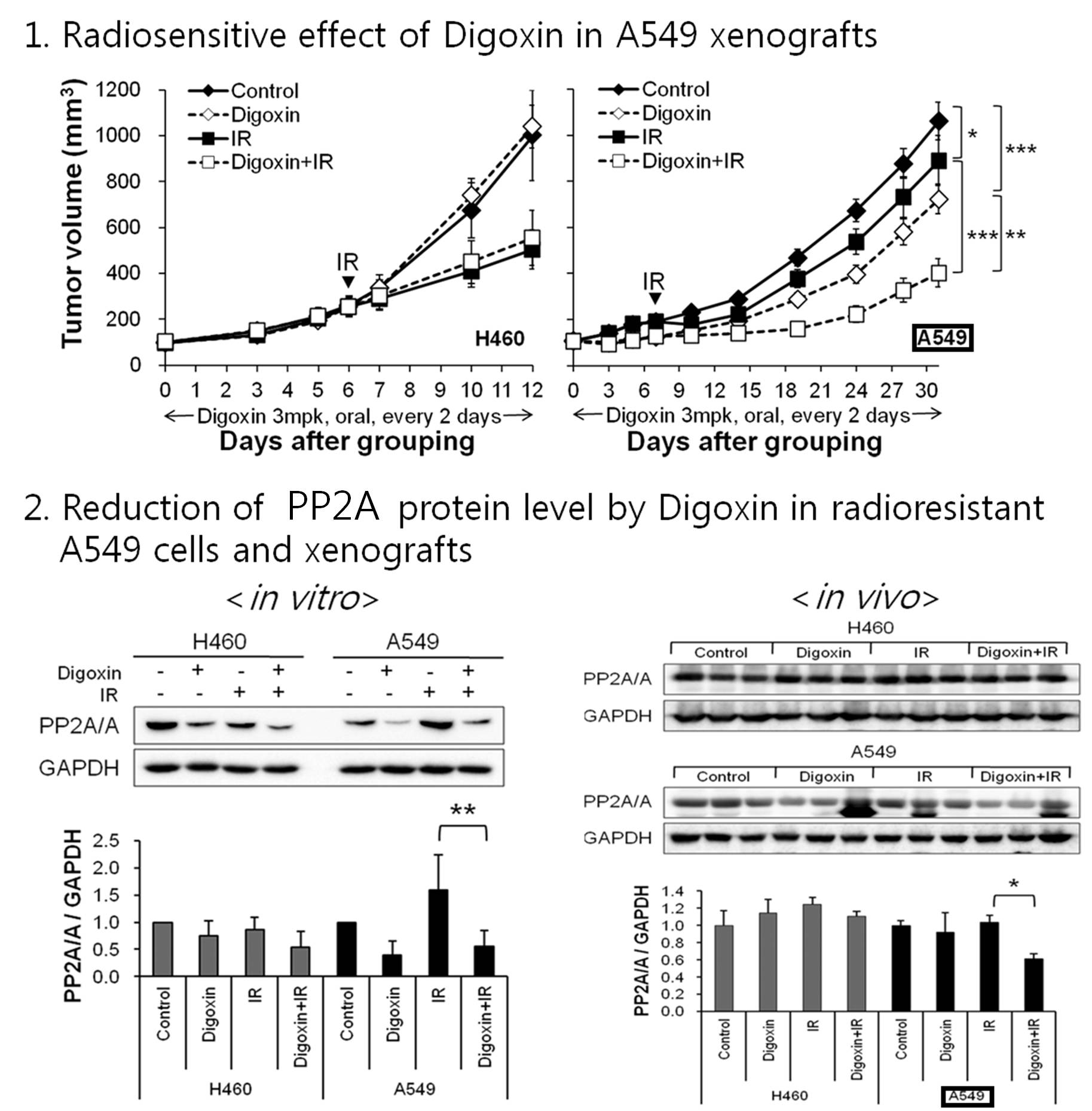
Protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) is a ubiquitous multifunctional enzyme usually known as a tumor suppressor. Recent studies have reported that although inhibition of PP2A leads to acceleration of cell growth, it also induces damaged cells to pass through the cell cycle and renders them sensitive to radiotherapy. Here, we investigated the radiosensitizing effects of digoxin as a PP2A inhibitor in two non-small cell lung cancer cell types (H460 and A549) with differential sensitivity to radiation. Digoxin inhibited the proliferation of H460 and A549 cells in a dose-dependent fashion and was especially effective on radioresistant A549 cells. Interestingly, the radiosensitizing effect of digoxin was only present in the radioresistant A549 cells and xenografts. The combination of digoxin and ionizing radiation (IR) significantly reduced clonogenic survival and xenograft tumor growth ( P < 0.001), compared to IR alone. Digoxin suppressed PP2A protein expression and prevented IR-induced PP2A expression in A549 cells. Digoxin treatment combined with IR allowed the damaged cell to progress through the cell cycle via suppression of cell cycle-related proteins (p53, cyclin D1, cyclin B1, CDK4, and p-cdc2). Moreover, digoxin enhanced IR-induced DNA damage through reduction in levels of repair proteins and elevation of p-ATM foci formation up to 24 hours ( P < 0.001). In conclusion, digoxin has a novel function as a PP2A inhibitor, and combined with IR produces a synergistic effect of radiosensitizing cells, thereby indicating a potentially promising therapeutic approach to radioresistant lung cancer treatment.
Author information
Lee JY1, Kim MS2, Lee MS3, Ju JE3, Chung N4, Jeong YK5.
1Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, Seoul, Korea (South), Republic of.2Department of Radiation Oncology, Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, Seoul, Korea (South), Republic of.3Radiation Non-clinical Center, Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, Seoul, Korea (South), Republic of.4Department of Biosystems Engineering, Korea University, Seoul, Korea (South), Republic of.5Radiation non-clinical center, Korea Institute of Radiological & Medical Science, Seoul, N/A, 01812, Korea (South), Republic of amy3523@kirams.re.kr.
- 키워드
- Cardiac glycosides; PP2A inhibitor; radioresistance; radiosensitizer
- 연구소개
- 신약재창출을 통해 강심제로 사용되는 Digoxin이 항암방사선치료 민감제로 사용될 수 있는 가능성을 제시한 논문입니다. 방사선에 대한 내성을 가진 암세포인 A549 폐암세포주와 이종이식동물모델에서 Digoxin은 방사선내성인자로 알려진 단백질 중의 하나인 protein phosphatase 2A을 감소시킴으로서 방사선에 의한 항암효능을 증가시킬 뿐만 아니라 cell cycle arrest 및 DNA damage repair 기전을 저해함으로서 방사선 민감제 역할을 하고 있음을 규명하였습니다. 따라서, 최근 신약재창출을 통해 기존의 의약품을 방사선의학 연구에 활용한 좋은 예로서 연구자들의 아이디어 창출에 도움이 될 만한 정보라 생각합니다.
- 덧글달기









