글로벌 연구동향
방사선생물학
![[Radiat Oncol J.] Factors associated with pulmonary toxicity after myeloablative conditioning using fractionated total body irradiation.](/enewspaper/upimages/admin_20171110200948_R.jpg) [Radiat Oncol J.] Factors associated with pulmonary toxicity after myeloablative conditioning using fractionated total body irradiation.
[Radiat Oncol J.] Factors associated with pulmonary toxicity after myeloablative conditioning using fractionated total body irradiation.연세의대/ 변화경, 윤홍인*
- 출처
- Radiat Oncol J.
- 등재일
- 2017 Sep
- 저널이슈번호
- 35(3):257-267. doi: 10.3857/roj.2017.00290. Epub 2017 Sep 29.
- 내용
AbstractPURPOSE:
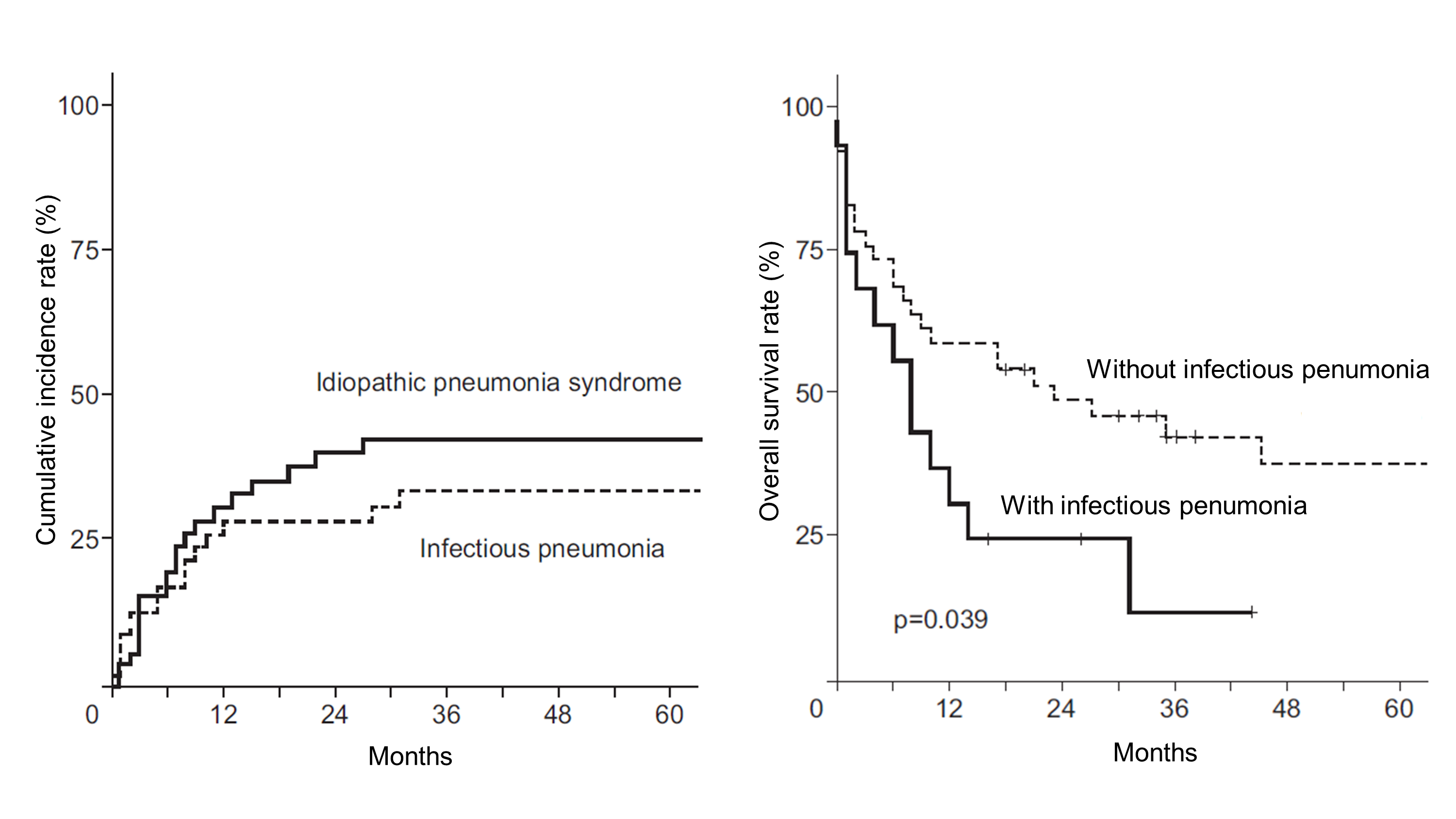
Pulmonary toxicities, including infectious pneumonia (IP) and idiopathic pneumonia syndrome (IPS), are serious side effects of total body irradiation (TBI) used for myeloablative conditioning. This study aimed to evaluate clinical factors associated with IP and IPS following TBI.
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
Fifty-eight patients with hematologic malignancies who underwent TBI before allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation between 2005 and 2014 were reviewed. Most patients (91%) received 12 Gy in 1.5 Gy fractions twice a day. Pulmonary toxicities were diagnosed based on either radiographic evidence or reduced pulmonary function, and were subdivided into IP and IPS based on the presence or absence of concurrent infection.
RESULTS:
Pulmonary toxicities developed in 36 patients (62%); 16 (28%) had IP and 20 (34%) had IPS. IP was significantly associated with increased treatment-related mortality (p = 0.028) and decreased survival (p = 0.039). Multivariate analysis revealed that the risk of developing IPS was significantly higher in patients who received stem cells from a matched unrelated donor than from a matched sibling donor (p = 0.021; hazard ratio [HR] = 12.67; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.46-110.30). Combining other conditioning agents with cyclophosphamide produced a higher tendency to develop IP (p = 0.064; HR = 6.19; 95% CI, 0.90-42.56).
CONCLUSION:
IP and IPS involve different risk factors and distinct pathogeneses that should be considered when planning treatments before and after TBI.
Author information
Byun HK1, Yoon HI1, Cho J1, Kim HJ1, Min YH2, Lyu CJ3, Cheong JW2, Kim JS2, Kim HS3, Kim SJ2, Yang AJ1, Lee BM1, Lee WH1, Lee J1, Ahn KJ4, Suh CO1.
1Department of Radiation Oncology, Yonsei Cancer Center, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.2Division of Hematology, Department of Internal Medicine, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.3Division of Pediatric Hemato-oncology, Department of Pediatrics, Yonsei University Health System, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.4Department of Radiation Oncology, Inje University Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 키워드
- Idiopathic pneumonia syndrome; Infectious pneumonia; Stem cell transplantation; Total body irradiation
- 연구소개
- Total body irradiation (TBI) 후 발생하는 폐렴은 조혈모 세포 이식 후 사망률을 높이는 심각한 부작용입니다. 본 논문에서는 TBI 시행 후 발생하는 폐렴과 관련 있는 위험 요인을 밝히고자 하였습니다. 특히, 비혈연간 이식이 특발성 폐렴의 발생률을 높이고, 여러 개의 전처치제가 사용된 경우 감염성 폐렴의 발생률을 높이는 것으로 나타났습니다. 이러한 위험 요인이 있는 환자를 TBI 시행 전 미리 인지하고, 치료 계획에 반영할 수 있도록 도움을 줄 수 있는 정보라 생각합니다.
- 덧글달기









