글로벌 연구동향
의학물리학
- [Phys Med Biol.] Experimental evaluation of convolutional neural network-based inter-crystal scattering recovery for high-resolution PET detectors
서울대 / 이승은, 이재성*
- 출처
- Phys Med Biol.
- 등재일
- 2023 Apr 26
- 저널이슈번호
- 68(9). doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/accacb.
- 내용
Abstract
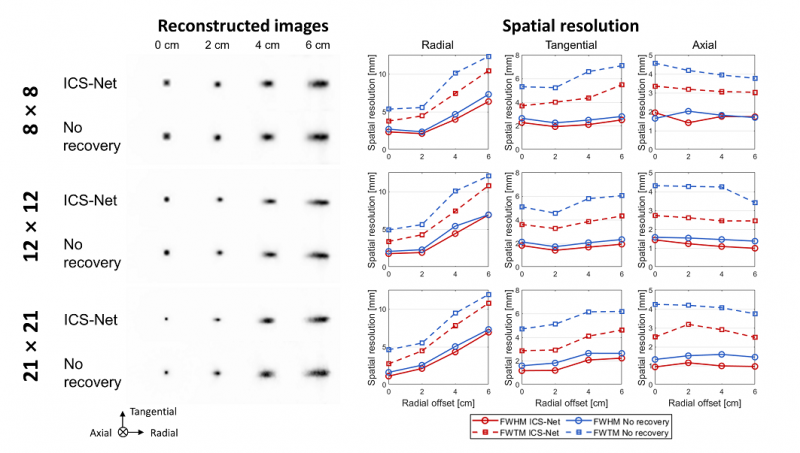
Objective. One major limiting factor for achieving high resolution of positron emission tomography (PET) is a Compton scattering of the photon within the crystal, also known as inter-crystal scattering (ICS). We proposed and evaluated a convolutional neural network (CNN) named ICS-Net to recover ICS in light-sharing detectors for real implementations preceded by simulations. ICS-Net was designed to estimate the first-interacted row or column individually from the 8 × 8 photosensor amplitudes.Approach. We tested 8 × 8, 12 × 12, and 21 × 21 Lu2SiO5arrays with pitches of 3.2, 2.1, and 1.2 mm, respectively. We first performed simulations to measure the accuracies and error distances, comparing the results to previously studied pencil-beam-based CNN to investigate the rationality of implementing fan-beam-based ICS-Net. For experimental implementation, the training dataset was prepared by obtaining coincidences between the targeted row or column of the detector and a slab crystal on a reference detector. ICS-Net was applied to the detector pair measurements with moving a point source from the edge to center using automated stage to evaluate their intrinsic resolutions. We finally assessed the spatial resolution of the PET ring.Main results. The simulation results showed that ICS-Net improved the accuracy compared with the case without recovery, reducing the error distance. ICS-Net outperformed a pencil-beam CNN, which provided a rationale to implement a simplified fan-beam irradiation. With the experimentally trained ICS-Net, the degree of improvements in intrinsic resolutions were 20%, 31%, and 62% for the 8 × 8, 12 × 12, and 21 × 21 arrays, respectively. The impact was also shown in the ring acquisitions, achieving improvements of 11%-46%, 33%-50%, and 47%-64% (values differed from the radial offset) in volume resolutions of 8 × 8, 12 × 12, and 21 × 21 arrays, respectively.Significance. The experimental results demonstrate that ICS-Net can effectively improve the image quality of high-resolution PET using a small crystal pitch, requiring a simplified setup for training dataset acquisition.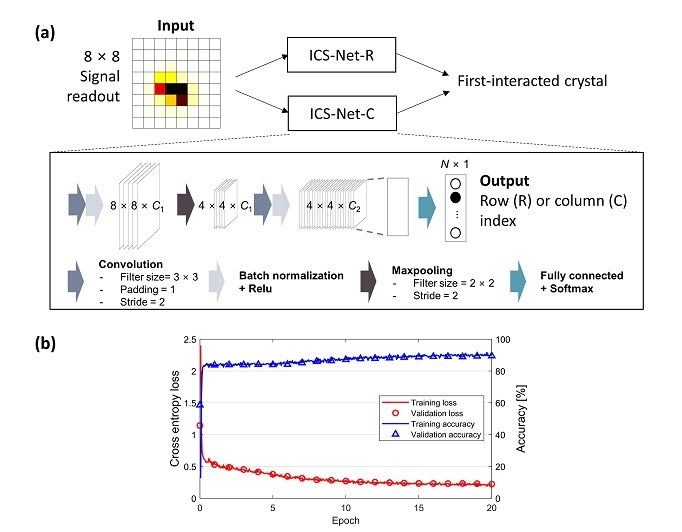
Affiliations
Seungeun Lee 1 2, Jae Sung Lee 1 3
1Department of Nuclear Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, 03080, Republic of Korea.
2Department of Biomedical Sciences, Seoul National University, Seoul, 03080, Republic of Korea.
3Brightonix Imaging Inc., Seoul, 04782, Republic of Korea.
- 키워드
- PET detectors; convolutional neural network; high-resolution PET; inter-crystal scattering; machine learning.
- 연구소개
- PET의 공간 분해능을 저해하는 크리스탈 간 산란 (inter-crystal scattering; ICS)을 보정하는 합성 곱 신경망 (convolutional neural network; CNN)을 개발, 실험적으로 보정 효과를 평가하였습니다. 이 CNN은 크리스탈 배열로부터 신호를 읽는 Digital Photon Counter의 신호 배열을 기반으로 511 keV 광자의 첫째 반응 위치를 추정합니다. 다양한 크기의 크리스탈 배열로 검출기를 구성하였으며, CNN 적용 시 모든 경우에 대해 공간 분해능이 개선되었습니다. 특히 ICS가 많이 발생하는 작은 크리스탈의 검출기에서 특히 개선이 크게 이루어짐으로써 (최대 62%), 고해상도를 요구하는 소동물 및 organ-dedicated PET에서 CNN 기반 ICS 보정의 효과가 클 것으로 기대할 수 있었습니다.
- 덧글달기









