글로벌 연구동향
분자영상 및 방사화학
- [ACS Nano .] Circulation Time-Optimized Albumin Nanoplatform for Quantitative Visualization of Lung Metastasis via Targeting of Macrophages대식세포 표적화를 통한 폐 전이의 정량적 시각화를 위한 순환 시간 최적화 알부민 나노 플랫폼
서울대 / 정혜원, 박지용, 이윤상*, 석승혁*
- 출처
- ACS Nano .
- 등재일
- 2022 Aug 9
- 저널이슈번호
- 16(8):12262-12275. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.2c03075. Online ahead of print.
- 내용
-
Abstract
The development of molecular imaging probes to identify key cellular changes within lung metastases may lead to noninvasive detection of metastatic lesions in the lung. In this study, we constructed a macrophage-targeted clickable albumin nanoplatform (CAN) decorated with mannose as the targeting ligand using a click reaction to maintain the intrinsic properties of albumin in vivo. We also modified the number of mannose molecules on the CAN and found that mannosylated serum albumin (MSA) harboring six molecules of mannose displayed favorable pharmacokinetics that allowed high-contrast imaging of the lung, rendering it suitable for in vivo visualization of lung metastases. Due to the optimized control of functionalization and surface modification, MSA enhanced blood circulation time and active/passive targeting abilities and was specifically incorporated by mannose receptor (CD206)-expressing macrophages in the metastatic lung. Moreover, extensive in vivo imaging studies using single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)/CT and positron emission tomography (PET) revealed that blood circulation of time-optimized MSA can be used to discern metastatic lesions, with a strong correlation between its signal and metastatic burden in the lung.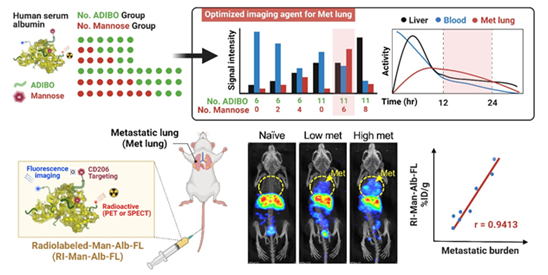
알부민 나노플랫폼을 활용하여 종양 마크로파지에 선택적으로 반응해 신호를 발생시킬 수 있는 이미지 프로브를 개발하였으며, 이를 이용하여 비침습적 폐 전이 진단 가능성을 검증하였음
Affiliations
Hyewon Chung 1 2, Ji Yong Park 3 4 5 6, Kyuwan Kim 4 5, Ran Ji Yoo 4 5, Minseok Suh 7, Gyo Jeong Gu 1, Jin Sil Kim 4, Tae Hyeon Choi 4 7, Jung Woo Byun 4, Young Wook Ju 8, Wonshik Han 8, Han Suk Ryu 9, Gehoon Chung 6 10, Do Won Hwang 4 11, Yujin Kim 3, Hye-Ryun Kang 3, Yi Rang Na 12, Hongyoon Choi 4, Hyung-Jun Im 7 13, Yun-Sang Lee 3 4 5, Seung Hyeok Seok 1 3
1Macrophage Lab, Department of Microbiology and Immunology, and Institute of Endemic Disease, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 03080, Republic of Korea.
2Bio-MAX Institute, Seoul National University, Seoul 03080, Republic of Korea.
3Department of Biomedical Sciences, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 03080, Republic of Korea.
4Department of Nuclear Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul 03080, Republic of Korea.
5Cancer Research Institute, Seoul National University, Seoul 03080, Republic of Korea.
6Dental Research Institute, Seoul National University, Seoul 03080, Republic of Korea.
7Department of Molecular Medicine and Biopharmaceutical Sciences, Graduate School of Convergence Science and Technology, Seoul National University, Seoul 03080, Republic of Korea.
8Department of Surgery and Cancer Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 03080, Republic of Korea.
9Department of Pathology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 03080, Republic of Korea.
10Department of Oral Physiology, Seoul National University, School of Dentistry, Seoul 03080, Republic of Korea.
11Research and Development Center, THERABEST, Co. Ltd., Seoul 03080, Republic of Korea.
12Transdisciplinary Department of Medicine and Advanced Technology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul 03080, Republic of Korea.
13Research Institute for Convergence Science, Seoul National University, Seoul 08823, Republic of Korea.
- 키워드
- albumin nanoplatform; blood circulation; lung metastasis; macrophage; noninvasive imaging.
- 연구소개
- 본 연구는 알부민 나노플랫폼을 이용하여 전이소에 존재하는 종양 마크로파지를 생체이미징할 수있는 이미징 프로브를 개발하였으며, 이는 기존처럼 암세포 자체가 아닌 주변의 종양 미세환경을 타겟함으로써 비침습적 전이 진단이 가능함을 제시하였다. 암 치료의 또 다른 주요 시점은 원발 종양제거 수술 및 항암치료가 끝난 바로 그 시점이며, 이때 암환자 완치 및 전이 재발 억제를 위해서는 환자의 정확한 종양 전이 여부 판단 및 각 환자에게 적절한 향후 치료전략이 중요하다. 최근에는 microRNA를 포함하여 다양한 연구를 바탕으로 발견된 바이오마커를 혈액검사로 판단함으로써 전이를 진단하고자 하는 시도가 있지만 이는 전반적인 종양 진행 정도 또는 예후에 대한 지표 중의 하나로 의미가 있을 뿐, 전이 여부 또는 구체적인 전이 위치 등의 정보를 제공해주기에는 부족하다. 또한 조직 생검 검사는 침습적이라서 지속적으로 환자에게 시행하기 어렵고, 전이의 전신분포를 장기간 정기적 추적 검사하기 어렵다는 점에서 한계가 있다. 원발암에서 떨어져 나온 암세포가 이차 장기에 저악하여 전이암으로 성장하기 위해서 암세포는 전이 장기내 자신에게 우호적인 종양 미세환경을 형성한다. 본 연구팀은 전이 미세환경을 형성하여 암세포의 전이를 도와주는 종양 마크로파지가 만노즈 수용체(CD206)를 과발현하고 있다는 사실에 착안하여 이를 타겟하여 생체 이미징 가능한 프로브를 개발하였다. 생체 유사 단백질인 알부민 나노플랫폼을 활용하여 전이암 내 종양 마크로파지에 선택적으로 반응하여 신호를 발생시킬 수 있도록 최적화하였으며, 방사성 동위원소를 표지한 프로브를 유방암 폐진이 마우스 모델에 주입 시 폐에서 신호가 증가하는 것을 SPECT, PET 영상으로 각각 관찰하였다. 또한 개발된 프로브 기술은 전신영상에서 신호의세기가 전이 정도와 상관관계가 높으며 작은 크기의 미세암 전이를 진단 가능함을 확인하여 전이암의 조기 발견 및 진단에 큰 도움이 될 것으로 전망된다.
- 덧글달기









