글로벌 연구동향
방사선방호 및 안전
- [Phys Med Biol.] Development of advanced skin dose evaluation technique using a tetrahedral-mesh phantom in external beam radiotherapy: a Monte Carlo simulation study.외부 방사선치료 시 Tetrahedral-mesh 팬텀을 이용한 피부선량 고급평가기술 개발: 몬테카를로 전산모사 연구
연세대 / 천보위, 유도현, 신욱근, 최현준, 박효준, 김정인, 민철희*
- 출처
- Phys Med Biol.
- 등재일
- 2019 Aug 14
- 저널이슈번호
- 64(16):165005. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ab2ef5.
- 내용
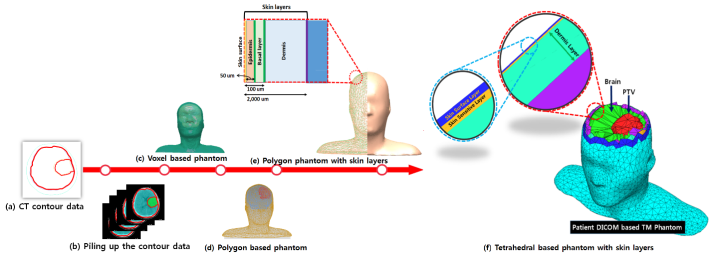
환자 CT를 기반으로 얇은 피부층을 포함한 사면체 면 기반 모의피폭체를 제작하는 과정
Abstract
Incorrect prediction of skin dose in external beam radiotherapy (EBR) can have normal tissue complication such as acute skin desquamation and skin necrosis. The absorbed dose of skin should be evaluated within basal layer, placed between the epidermis and dermis layers. However, current treatment planning systems (TPS) cannot correctly define the skin layer because of the limitation of voxel resolution in computed tomography (CT). Recently, a new tetrahedral-mesh (TM) phantom was developed to evaluate radiation dose realistically. This study aims to develop a technique to evaluate realistic skin dose using the TM phantom in EBR. The TM phantom was modeled with thin skin layers, including the epidermis, basal layer, and dermis from CT images. Using the Geant4 toolkit, the simulation was performed to evaluate the skin dose according to the radiation treatment conditions. The skin dose was evaluated at a surface depth of 50 µm and 2000 µm. The difference in average skin dose between depths was up to 37%, depending on the thickness and region of the skin to be measured. The results indicate that the skin dose has been overestimated when the skin is evaluated using commercial TPS. Although it is not possible with traditional TPS, our skin dose evaluation technique can realistically express the absorbed dose at thin skin layers from a patient-specific phantom.
Author informationCheon BW1, Yoo DH, Shin WG, Choi HJ, Park HJ, Kim JI, Min CH.
1
Department of Radiation Convergence Engineering, Yonsei University, Wonju 26493, Republic of Korea.
- 연구소개
- 본 논문은 몬테칼로 전산모사 기반 치료방사선에 대하여 더 현실적으로 피부선량을 평가하는 기술개발에 대한 연구내용을 포함하고 있습니다. 국제방사선방호위원회(International Commission on Radiological Protection, ICRP)에 따르면 피부선량은 방사선민감층인 기저층(Basal layer)에서 평가되어야 한다고 권고하고 있습니다. 이러한 기저층은 피부 표면으로부터 약 50 um 깊이에서 50um 두께의 매우 얇은 범위를 가지며 존재하고, 평균적으로 약 70 um 위치에 존재합니다. 하지만, 현재 통상의 치료계획시스템(Treatment Planning Systems, TPS)은 컴퓨터단층촬영(Computed Tomography image, CT) 영상의 해상도한계로 인하여 매우 얇은 기저층을 정확히 표현하는 데에는 다소 어려움이 있습니다. 반면, 최근 개발된 사면체 면 기반의 인체모의피폭체(Tetrahedral-Mesh based Computational Phantom)는 매우 작은 형태의 장기부터 복잡한 형태의 장기까지 현실적으로 표현 할 수 있는 장점이 있습니다. 따라서, 본 연구에서는 실제 환자의 CT 영상을 통해 환자의 피부면을 사면체 면 기반의 모의피폭체로 변환 한 뒤, 이를 이용하여 방사선 치료 전 환자에게 전달되는 피부선량을 더 현실적으로 평가할 수 있는 피부선량 평가기술 개발을 목적으로 합니다.
- 덧글달기









