글로벌 연구동향
분자영상 및 방사화학
- [Theranostics.] Dysregulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine 6 receptor accelerates maturation of bone-resorbing osteoclasts and induces bone loss.
경희대 / 박경란, 윤형문*
- 출처
- Theranostics.
- 등재일
- 2018 Apr 30
- 저널이슈번호
- 8(11):3087-3098. doi: 10.7150/thno.24426. eCollection 2018.
- 내용
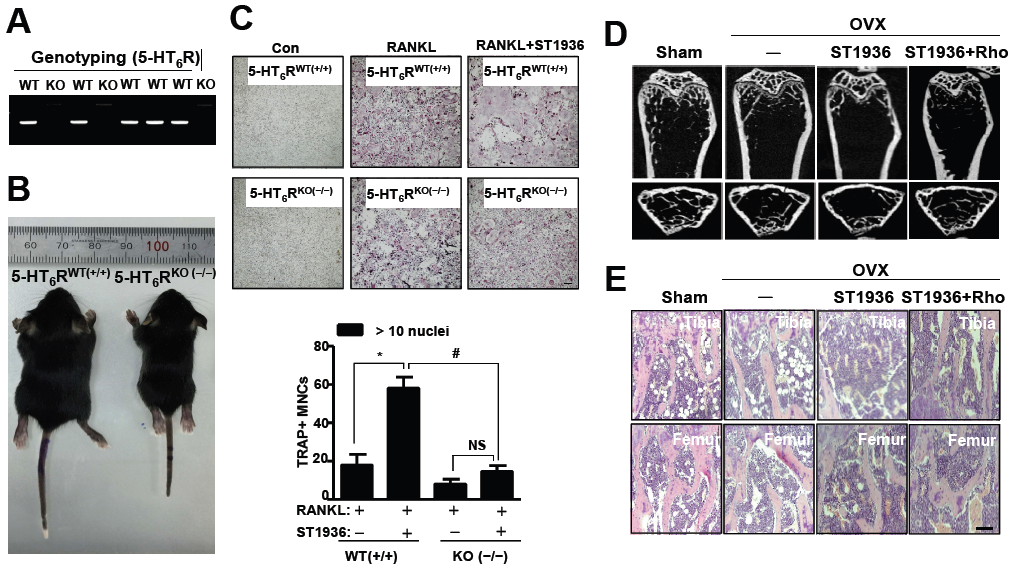
(A-C) 5-HT6R 유전자가 결여된 쥐(5-HT6R knock-out mice)의 골수에서 추출한 대식세포(BMM)를 파골세포로 분화시켰을 때, 5-HT6R의 영향 분석
(D-E) 5-HT6R를 통한 골다공증 동물모델에서 μCT 및 조직학적으로 골흡수 정도를 분석
Abstract
Rationale: Characterizing the regulation of bone-resorbing osteoclasts is central to the understanding of the pathogenesis and treatment of bone diseases, such as osteoporosis and periodontitis. 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) has drawn considerable attention for its role in bone; however, it remains unknown whether the intracellular signaling of 5-HT receptors (5-HTRs) is linked to any of the regulatory mechanisms in osteoclasts. Herein, we report 5-HT6R to be a key regulatory receptor for osteoclastogenesis. Methods: In order to explore the critical role of 5-HT6R in bone-resorbing osteoclasts, in vitro experiments were performed using mouse whole bone marrow cells isolated from femora and tibiae and In vivo animal experiments were performed using 5-HT6R-deficient (5-HT6RKO-/-) mice, bone resorption mice model, and osteoporosis mice model. Results: Compared to other 5HTRs, activation of 5-HT6R relatively increased TRAP (tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase) activity during osteoclastogenesis. 5-HT6RKO(-/-) mice and 5-HT6RKO(-/-) osteoclast lineages presented with an abnormal phenotype and impaired osteoclastogenesis and impaired osteoclastogenesis. Activation of 5-HT6R increased the number of TRAP-positive multinuclear osteoclasts, actin ring formation, and expression of early osteoclast markers with osteoclast lineage commitment. Intracellular 5-HT6R signaling was found to be linked to RhoA GTPase activation and was involved in the maturation of osteoclasts. This signaling pathway also showed enhanced bone destruction after lipopolysaccharide (LPS) administration in mice. Furthermore, inhibition of 5-HT6R-mediated RhoA GTPase signaling protected against ovariectomy(OVX)-induced bone loss in mice. Conclusion: Taken together, our findings place the 5-HT6R system in a new context of osteoclast lineages in both an in vitro and in vivo system, and also it may offer a novel molecular target for the treatment of bone diseases.
Author informationPark KR1, Kim EC2, Hong JT1, Yun HM2.
1
College of Pharmacy and Medical Research Center, Chungbuk National University, Chungbuk 194-31, Republic of Korea.
2
Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology, School of Dentistry, Kyung Hee University, Seoul 130-701, Republic of Korea.
- 키워드
- 5-HT6R; RhoA GTPase; osteoclast; osteoporosis
- 연구소개
- 신경계에서 잘 알려진 세로토닌 6 수용체(5-HT6R)에 대한 골격계 작용 기전 및 대사성 골질환과의 연관성을 연구한 것입니다. 5-HT6R 유전자가 결여 쥐, 두개골 골흡수 동물모델, 그리고 골다공증 동물모델에서 뼈에 대한 μCT 분석과 세포/조직학적 분석을 통해 5-HT6R의 신규 기능을 규명한 것입니다.
- 덧글달기










편집위원
파골세포(Osteoclasts)의 작동과 관련하여 5-hydroxytryptamine(5-HT)의 역할은 중요하게 고려되어 왔다. 이 논문에서는 5-HT의 작용과 관련한 주요 수용체로써의 5-HT6R의 중요성을 in vitro 및 KO 마우스(5-HT6RKO(-/-))등을 이용한 in vivo 실험을 통해 보고하면서 뼈질환 치료를 위한 가능성을 제시하고 있다.
2018-12-14 16:56:53