글로벌 연구동향
분자영상 및 방사화학
- 2017년 12월호
[Biomaterials.] Polyglycerolated nanocarriers with increased ligand multivalency for enhanced in vivo therapeutic efficacy of paclitaxel.한양대학교,KAIST,/ Trang Huyen Le Kim, 유종헌, 전휘석, 김진웅*, 김지선*, 남윤성*
- 출처
- Biomaterials.
- 등재일
- 2017 Nov
- 저널이슈번호
- 145:223-232. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.08.042. Epub 2017 Aug 29.
- 내용
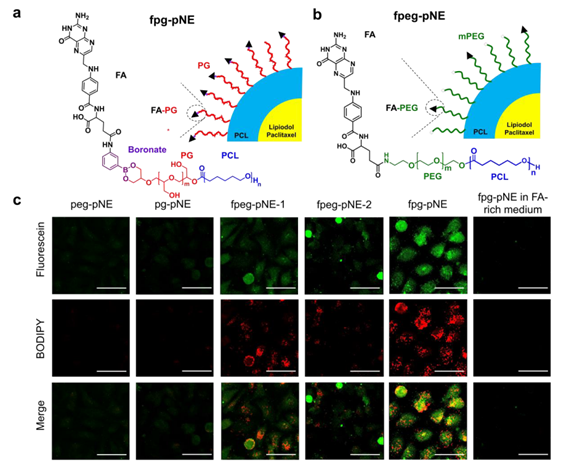
(a) polyglycerol nanoemulsion (pg-NE)에 folate를 도입하여 제조된 fpg-NE 구조식
(b) polyethylenglycol에 folate를 도입하여 제조한 fpeg-NE의 구조식
(c) Nanoemulsion을 처리한 HeLa cell의 confocal fluorescence microscopic images ( peg-pNE, pg-pNE, fpeg-pNE-1, fpeg-pNE-2, and fpg-pNE containing fluorescein-PCL (green) and BODIPY® -paclitaxel (red). Scale bars = 10 μm).
Abstract
Despite the excellent biocompatibility and antifouling effect of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG), the high steric hindrance, limited chemical functionality, and low ligand multivalency of PEGylated nanocarriers often lead to inefficient cell targeting and intracellular trafficking. Hence, a new structure of hydrophilic corona allowing a higher ligand density without loss of excellent biocompatibility is highly desirable. Here we introduce tumor-targeted polyglycerolated (PGylated) nanocarriers that dramatically enhance the in vivo therapeutic efficacy of incorporated paclitaxel simply by increasing the surface density of hydrophobic tumor-targeting ligands. Linear polyglycerol-poly (ε-caprolactone) block copolymer (PG-b-PCL) is used to prepare PGylated lipiodol nanoemulsions, where PG serves as a corona conjugated with a large number of folic acid (FA) for efficient tumor targeting. Unlike FA-PEGylated nanoemulsions, FA-PGylated nanoemulsions can display a larger number of FA without structural destabilization. This property enables excellent anti-cancer activities and effective tumor regression in a cervical cancer xenograft murine model at a cumulative drug dose of ∼5 mg kg-1, which is about four fold smaller than that of commercial Taxol formulation. This study highlights the importance of surface chemistry of nanocarriers that enable multivalent ligand functionalization and high tolerance to the conjugation of hydrophobic ligands, which make PG as a very effective hydrophilic corona for in vivo drug delivery.
Author informationLe Kim TH1, Yu JH1, Jun H1, Yang MY2, Yang MJ3, Cho JW3, Kim JW4, Kim JS5, Nam YS6.
1
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, 291 Daehak-ro, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon, 34141, Republic of Korea.
2
KAIST Institute for the NanoCentury, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, 291 Daehak-ro, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon, 34141, Republic of Korea.
3
Pathology Research Group, Jeonbuk Department of Inhalation Research, Korea Institute of Toxicology, 30 Baekhak 1-gil, Jeongeup, Jeonbuk, 56212, Republic of Korea.
4
Department of Bionano Technology, Hanyang University, 55 Hanyangdaehak-ro, Sangnok-gu, Ansan, Gyeonggi-do, 426-791, Republic of Korea; Department of Chemical and Molecular Engineering, Hanyang University, 55 Hanyangdaehak-ro, Sangnok-gu, Ansan, Gyeonggi-do, 15588, Republic of Korea. Electronic address: kjwoong@hanyang.ac.kr.
5
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, 291 Daehak-ro, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon, 34141, Republic of Korea. Electronic address: eliekim@kaist.ac.kr.
6
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, 291 Daehak-ro, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon, 34141, Republic of Korea; KAIST Institute for the NanoCentury, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, 291 Daehak-ro, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon, 34141, Republic of Korea. Electronic address: yoonsung@kaist.ac.kr.
- 키워드
- Ligand multivalency; Linear polyglycerol; Nanoemulsions; Paclitaxel; Tumor targeting
- 연구소개
- 최근 수십년간 나노의학 분야에서 활용하는 물질은 유기소재를 넘어, 무기물, 유-무기 복합체, 탄소기반 나노물질 등으로 확대되어 왔으나, 활용물질의 생체 적합성을 결정하는 표면 처리 물질은 관한 연구들은 폴리에틸렌글리콜 (PEG)에 한정되어 있습니다. 그러나 PEG의 잠재적 독성에 대한 연구결과들이 발표되고 있으며, 뿐만 아니라 PEG 고분자 사슬의 합성 관능기 수가 적고, 사슬 유동성 (chain mobility)이 높아, 이를 이용하여 제조한 나노 물질의 세포 내 유입 효율이 낮아지는 문제점이 지적되고 있습니다. 본 연구에서는 폴리글리세롤(linear polyglycerol)를 친수성기로 갖는 고분자 나노에멀젼을 개발하였습니다. 즉, 폴리글리세롤 사슬에 존재하는 수산화기 (hydroxyl)를 활용하여 소수성 (hydrophobic)의 암세포 타겟팅 리간드를 나노에멀젼 표면에 분산 안정성을 유지하며 대량으로 도입하는 것에 성공함으로써, 기존의 PEG 기반 나노구조체들 보다 높은 암세포 타겟팅 효과를 갖는 것을 확인하였습니다. 이 나노에멀젼을 활용하여 기존의 Taxol 제형과 비교할 때, 약 75 % 감소된 약물 투여량만으로도 더 높은 암세포 사멸 효과를 유도할 수 있었습니다. 본 연구의 결과는 폴리글리세롤 고분자를 이용하여 새로운 생체 적합형 양친성 고분자를 개발하는 것을 넘어, 나노 의학 분야에서 PEG 의 내재적 단점을 극복할 수 있는 새로운 표면 물질의 대안을 제시하였다는 것에서 의의를 찾을 수 있을 것입니다.
- 덧글달기








편집위원
나노입자 연구에서 생체 적합한 사용을 위해 주로 PEG (poly(ethylene glycol))를 이용한 표면처리를 하는데 이는 장단점이 공존합니다. 이 연구에서는 PEG의 단점을 보완할 수 있도록 새롭게 개발한 polyglycerolated (PGylated) 나노입자를 보여주고 있습니다. 특히 엽산 (folic acid)과 paclitaxel을 도입하여 종양 표적 및 치료가 가능한 나노이멀젼을 만들고, 이를 이용한 동물 종양모델의 in vivo 결과를 바탕으로 새롭게 도입한 PG 표면의 유용성을 제시하고 있습니다.
덧글달기닫기2017-12-12 15:43:45
등록