글로벌 연구동향
방사선생물학
- [Int J Mol Sci.] RIP1 Is a Novel Component of γ-ionizing Radiation-Induced Invasion of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells 폐암에서의 방사선치료표적으로서의 RIP1의 역할
KIRAMS / 강아람, 박종국*
- 출처
- Int J Mol Sci.
- 등재일
- 2020 Jun 28
- 저널이슈번호
- 21(13):E4584. doi: 10.3390/ijms21134584.
- 내용
-
Abstract
Abstract: Previously, we demonstrated that γ-ionizing radiation (IR) triggers the invasion/migration of A549 cells via activation of an EGFR-p38/ERK-STAT3/CREB-1-EMT pathway. Here, we have demonstrated the involvement of a novel intracellular signaling mechanism in γ-ionizing radiation (IR)-induced migration/invasion. Expression of receptor-interacting protein (RIP) 1 was initially increased upon exposure of A549, a non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell line, to IR. IR-induced RIP1 is located downstream of EGFR and involved in the expression/activity of matrix metalloproteases (MMP-2 and MMP-9) and vimentin, suggesting a role in epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Our experiments showed that IR-induced RIP1 sequentially induces Src-STAT3-EMT to promote invasion/migration. Inhibition of RIP1 kinase activity and expression blocked induction of EMT by IR and suppressed the levels and activities of MMP-2, MMP-9 and vimentin. IR-induced RIP1 activation was additionally associated with stimulation of the transcriptional factor NF-κB. Specifically, exposure to IR triggered NF-κB activation and inhibition of NF-κB suppressed IR-induced RIP1 expression, followed by a decrease in invasion/migration as well as EMT. Based on the collective results, we propose that IR concomitantly activates EGFR and NF-κB and subsequently triggers the RIP1-Src/STAT3-EMT pathway, ultimately promoting metastasis.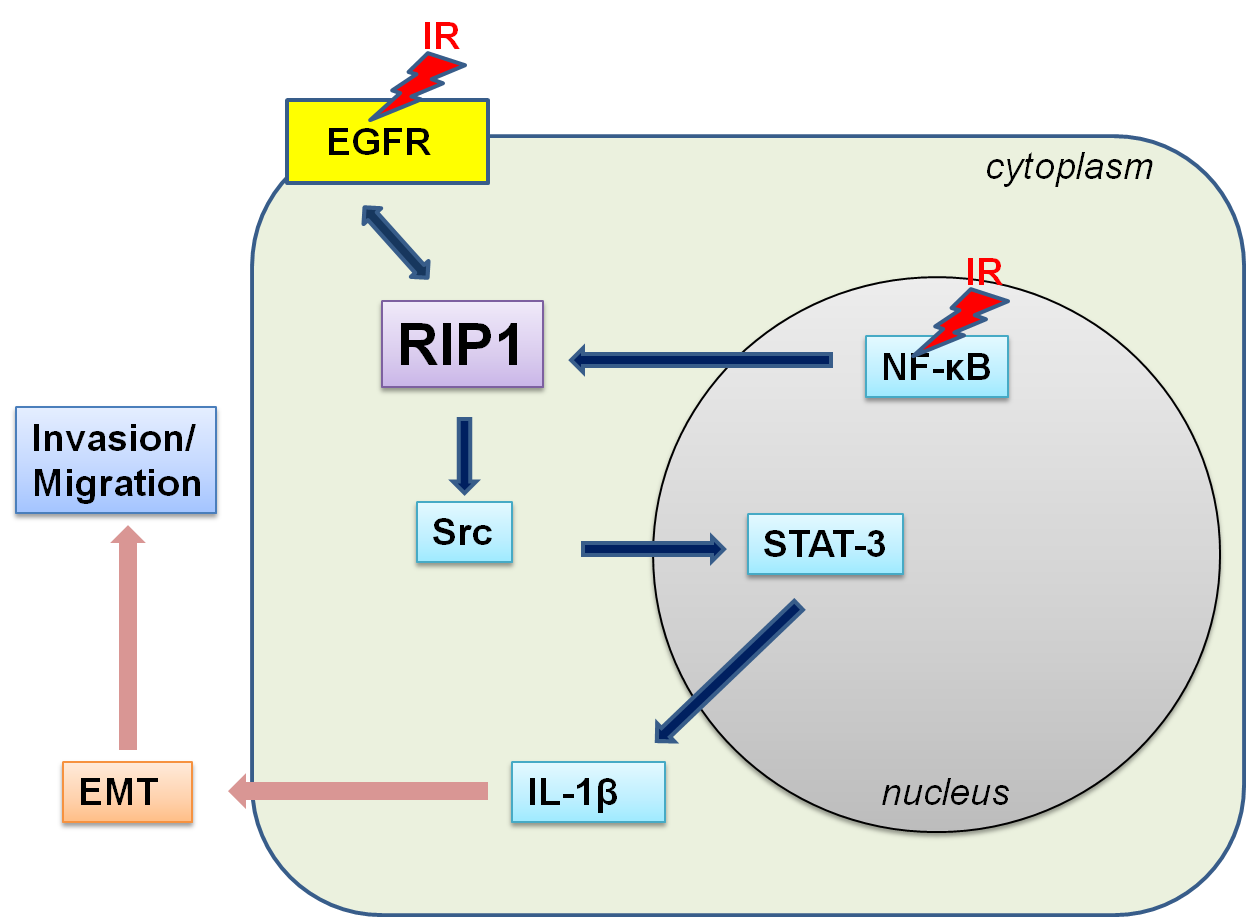
AffiliationsA-Ram Kang 1 , Jeong Hyun Cho 1 , Na-Gyeong Lee 1 , Jie-Young Song 1 , Sang-Gu Hwang 1 , Dae-Hee Lee 2 , Hong-Duck Um 1 , Jong Kuk Park 1
1 Division of Radiation Biomedical Research, Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, Seoul 01812, Korea.
2 Department of Marine Food Science and Technology, Gangneung-Wonju National University, 120 Gangneung, Gangwon 210-702, Korea.
- 키워드
- cancer invasion; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; non-small cell lung cancer; signal transduction; tumor microenvironment; γ-ionizing radiation.
- 연구소개
- 본 연구 논문은 RIP1 단백질의 새로운 기전을 규명한 논문입니다 염증 및 apoptosis/necroptosis에 주로 작동을 하는 RIP1 단백질이 방사선에 의하여 발현이 증가됨을 규명하였습니다 추가적으로 RIP1의 발현 증가는 기존에 알려진 방사선에 의한 EGFR과 NF-κB의 하부에 위치한 반응임을 규명하였습니다. 따라서 EGFR/NF-κB – RIP1 – Src – STAT3 – IL-1β의 신호 전달 기전을 구성함을 밝혀냈습니다 이 신호 전달 기전의 활성화는 EMT 기전을 활성화시켜 암세포의 침윤 증가 및 이동성 증가를 촉진시키게 됨을 세포 및 동물 실험 수준에서 규명하였습니다 이러한 연구 결과는 아래의 그림으로 정리하였습니다
- 덧글달기









