글로벌 연구동향
방사선생물학
- [Clin Cancer Res.] The Hsp27-Mediated IkB α-NFkB Signaling Axis Promotes Radiation-Induced Lung Fibrosis.Hsp27-NF-kB신호를 통한 방사선폐손상 조절연구
이화여대 / 김지윤, 이윤실*
- 출처
- Clin Cancer Res.
- 등재일
- 2019 May 24. pii: clincanres.3900.2018. doi: 10.11
- 저널이슈번호
- 내용
Abstract
PURPOSE:
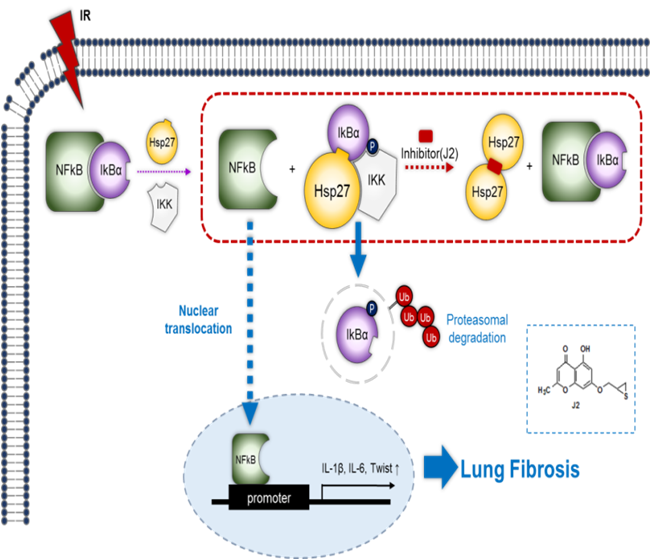
Lung fibrosis is a major side effect experienced by patients after lung cancer radiotherapy. However, effective protection strategies and underlying treatment targets remain unclear. In an effort to improve clinical outcomes, pharmacologic treatment of fibrosis is becoming increasingly popular; however, no ideal therapeutic strategy is yet available. Experimental Design/ Results: The expression of Hsp27 (Hsp27 in humans and Hsp25 in mice) was increased during radiation (IR)-induced lung fibrosis in a mouse model following IR. Exacerbation of lung fibrosis by IR was also found in Hsp25 transgenic (TG) mice. Knockdown of Hsp27 in lung epithelial cells inhibited IR-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). J2, a synthetic small molecule inhibitor of Hsp27, significantly alleviated lung fibrosis by IR in control and TG mice, and the therapeutic effects were better than those achieved with pirfenidone and amifostine. The activation of NFkB pathways via direct interaction between Hsp27 and IkBα resulted in increased expressions of Twist, IL-1β, and IL-6 and facilitated IR-mediated EMT, which was identified as an underlying mechanism of Hsp27-mediated fibrosis after IR. Hsp27 was overexpressed in IR-induced lung fibrosis in an orthotopic lung cancer model and was inhibited by J2 treatment. IR-induced lung fibrotic tissues from patients also showed higher expression of Hsp27 than unirradiated lungs.CONCLUSIONS:
Collectively, IkBα-NFkB signaling activation by Hsp27 is involved in the EMT process that is tightly connected to the development of IR-induced lung fibrosis. Our findings also suggest that inhibition of Hsp27 has the potential to become a valuable therapeutic strategy for IR-induced lung fibrosis.
Author informationKim JY1, Jeon S2, Yoo YJ2, Jin H2, Won HY3, Yoon K2, Hwang ES3, Lee YJ4, Na Y5, Cho J6, Lee YS7.
1
radiation oncology, Yonsei University College of Medicine.
2
College of Pharmacy & Division of Life & Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ewha Womans University.
3
College of Pharmacy, Ewha Womans University.
4
Division of Radiation Biomedical Research, Korea Instituteof Radiological and Medical Sciences.
5
College of Pharmacy, CHA University.
6
Radiation Oncology, Yonsei University College of Medicine.
7
College of Pharmacy, Ewha Womans University yslee0425@ewha.ac.kr.
- 연구소개
- 본 논문은 HSP27 단백질이 방사선에 의한 폐섬유화의 치료 타겟으로서의 가능성을 제시한 것으로 SBRT를 mimicking하는 마우스 방사선 조사에 의한 폐섬유화 과정에서 HSP27 단백질 증가를 확인한 논문입니다. 이러한 HSP27 증가에 의한 폐섬유화 유도는 HSP27의 NFkB의 활성화에 의한 Twist, IL1-beta 및 IL6 증가와 관련 있음을 유전자 이식 마우스 및 본 연구실에서 발굴한 HSP27의 기능적 저해 저분자물질을 이용하여 규명하였습니다.
- 덧글달기










편집위원
폐섬유증은 폐암의 방사선치료 과정에서 나타나는 대표적인 부작용이지만, 효과적인 치료법이 없는 상황이다. 본 연구에서는 Hsp27이 폐섬유증의 표적인자가 될 수 있음을 확인하였으며, Hsp27에 의한 IkBα-NFkB 신호경로의 활성화가 폐섬유증의 발달과 밀접한 관련이 있는 EMT에 관여함을 규명하였다.
2019-06-24 13:53:23
편집위원2
방사선에 의한 lung fibrosis 에 관여되는 분자세포학적인 조절 기전을 규명한 논문이라 사료됨
2019-06-24 13:53:58