글로벌 연구동향
핵의학
- [Sci Rep.] Prognostic value of 18F-FDG brain PET as an early indicator of neurological outcomes in a rat model of post-cardiac arrest syndrome.심정지 후 신경장애를 FDG PET으로 예측
이화의대 / 김대희, 윤혜전*
- 출처
- Sci Rep.
- 등재일
- 2019 Oct 15
- 저널이슈번호
- 9(1):14798. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-51327-1.
- 내용
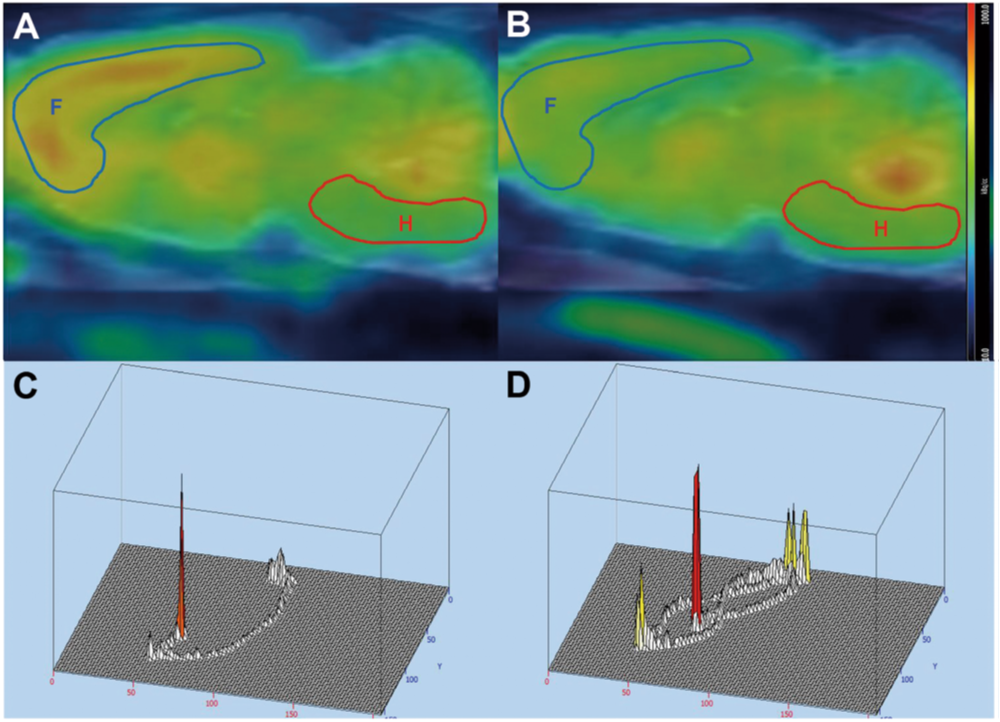
심정지 후 증후군 유도 3시간 후 촬영한 18F-FDG PET 의 시상면 (A-B)과 Morris water maze test 결과 (C-D)이다. 좌측은 신경학적 손상이 적은 그룹의 예시로서, 후뇌 (R로 표시된 빨간색 영역) 대비 전뇌 (F로 표시된 파란색 영역) 섭취비가 1.74였으며, maze test 수행에 소요된 시간과 거리는 각각 13.1분과 398.2 cm였다. 반면, 우측은 신경학적 손상이 많은 그룹의 예시로서, 후뇌 대비 전뇌 섭취비가 0.85였으며, maze test 수행에 소요된 시간과 거리는 각각 114.7분과 288.9 cm였다. 즉, 유도 후 3시간 PET 영상에서 후뇌 대비 전뇌 섭취비가 높을수록 양호한 신경학적 손상을 보인다.
Abstract
Predicting neurological outcomes in patients with post-cardiac arrest syndrome (PCAS) is crucial for identifying those who will benefit from intensive care. We evaluated the predictive value of 18F-FDG PET. PCAS was induced in Sprague Dawley rats. Baseline and post-3-hour images were acquired. Standardized uptake value (SUV) changes before and after PCAS induction (SUVdelta) and SUV ratios (SUVR) of regional SUV normalized to the whole brain SUV were obtained. The Morris water maze (MWM) test was performed after 2 weeks to evaluate neurological outcomes and rats were classified into two groups based on the result. Of 18 PCAS rats, 8 were classified into the good outcome group. The SUVdelta of forebrain regions were significantly decreased in good outcome group (p < 0.05), while the SUVdelta of hindbrain regions were not significantly different according to outcomes. The SUVR of forebrain regions were significantly higher and the SUVR of hindbrain regions were significantly lower in good outcome group (p < 0.05). Forebrain-to-hindbrain ratio predicted a good neurological outcome with a sensitivity of 90% and specificity of 100% using an optimal cutoff value of 1.22 (AUC 0.969, p < 0.05). These results suggest the potential utility of 18F-FDG PET in the early prediction of neurological outcomes in PCAS.
Author informationKim D1, Yoon HJ2, Lee WJ3, Woo SH3, Kim BS4.
1
Department of Emergency Medicine, Incheon St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Incheon, Korea.
2
Department of Nuclear Medicine, College of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea. haijeon.yoon@gmail.com.
3
Department of Emergency Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
4
Department of Nuclear Medicine, College of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea.
- 연구소개
- 본 연구는 심정지 후 증후군 환자의 신경학적 예후를 평가하기 위한 영상 마커로서 18F-FDG PET의 적용가능성을 평가한 연구이다. In vivo PET study에서 심정지 후 증후군 동물 모델의 뇌실질 내 18F-FDG 재분포를 확인하였다. 재분포의 양상은 장기 신경학적 예후에 따라 차이를 보였으며, 특히 후뇌 대비 전뇌 섭취비 (forebrain-to-hindbrain ratio, FHR)는 높은 정확도로 심정지 후 증후군의 신경학적 예후를 예측함으로써, 초기 예후 평가를 위한 도구로서 18F-FDG PET 영상의 적용 가능성을 보여주었다.
- 덧글달기
- 이전글 [Oncology.] Role of 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography or Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography for the Detection of Recurrent Disease after Treatment of Malignant Melanoma.
- 다음글 [Sci Rep.] Common features of F-18 FDG PET/CT findings in Scrub Typhus: prospective study before and after antibiotics therapy.









