글로벌 연구동향
핵의학
- [Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging.] Diagnostic value of surveillance 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT for detecting recurrent esophageal carcinoma after curative treatment.
성균관의대 / 김수정, 최준영*
- 출처
- Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging.
- 등재일
- 2019 Aug
- 저널이슈번호
- 46(9):1850-1858. doi: 10.1007/s00259-019-04387-4. Epub 2019 Jun 20.
- 내용
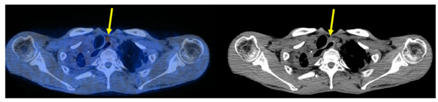
그림.1 FDG PET/CT로 좌측 종격동 림프절 전이를 조기 발견함(노랑 화살표)
Abstract
PURPOSE:
Esophageal carcinoma recurs within two years in approximately half of patients who receive curative treatment and is associated with poor survival. While 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) is a reliable method of detecting recurrent esophageal carcinoma, in most previous studies FDG PET/CT scans were performed when recurrence was suspected. The aim of this study was to evaluate FDG PET/CT as a surveillance modality to detect recurrence of esophageal carcinoma after curative treatment where clinical indications of recurrent disease are absent.METHODS:
A total of 782 consecutive FDG PET/CT studies from 375 patients with esophageal carcinoma after definitive treatment were reviewed. Abnormal lesions suggestive of recurrence on PET/CT scans were then evaluated. Recurrence was determined by pathologic confirmation or other clinical evidence within two months of the scan. If no clinical evidence for recurrence was found at least 6 months after the scan, the case was considered a true negative for recurrence.RESULTS:
The diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of PET/CT for detecting recurrent esophageal carcinomas were 100% (64/64) and 94.0% (675/718), respectively. There were no significant differences in the diagnostic performance of PET/CT for detecting recurrence according to initial stage or time between PET/CT and curative treatments. Unexpected second primary cancers were detected by FDG PET/CT in seven patients.CONCLUSIONS:
Surveillance FDG PET/CT is a useful imaging tool for detection of early recurrence or clinically unsuspected early second primary cancer in patients with curatively treated esophageal carcinoma but without clinical suspicion of recurrence.
Author informationKim SJ1, Hyun SH2, Moon SH2, Lee KS3, Sun JM4, Oh D5, Ahn YC5, Zo JI6, Shim YM6, Choi JY7.
1
Department of Nuclear Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, 29 Saemunan-ro, Jongno-gu, 03181, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
2
Department of Nuclear Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, 81 Irwon-ro, Gangnam-gu, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 06351.
3
Department of Radiology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
4
Division of Hematology-Oncology Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
5
Department of Radiation Oncology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
6
Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
7
Department of Nuclear Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, 81 Irwon-ro, Gangnam-gu, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 06351. jynm.choi@samsung.com.
- 키워드
- 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose; Esophageal cancer; Nuclear medicine; PET/CT; Surveillance
- 연구소개
- 식도암의 근치적 치료 후 임상적으로 재발이 의심되지 않는 환자에서도 FDG PET/CT를 시행하였을 때 높은 민감도와 특이도로 조기 재발을 진단할 수 있음을 보여준 연구입니다. 또한 우연히 이차암을 발견하기도 하여 식도암 환자의 치료 후 관리에서 FDG PET/CT의 역할을 정립하는데 도움이 될 수 있을 것으로 기대합니다. 현재, 2014-2015년 FDG PET 급여기준 개정으로 현재는 암 무증상 조기재발 진단 목적으로는 FDG PET을 시행할 수 없는데, 이러한 연구결과를 바탕으로 급여기준 개정이 이루어지기를 바랍니다.
- 덧글달기
- 이전글 [Arthritis Rheumatol.] Development and Validation of an 18 F-Fluorodeoxyglucose-Positron Emission Tomography With Computed Tomography-Based Tool for the Evaluation of Joint Counts and Disease Activity in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis.
- 다음글 [Clin Nucl Med.] The Preventive Effect of Parotid Gland Massage on Salivary Gland Dysfunction During High-Dose Radioactive Iodine Therapy for Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: A Randomized Clinical Trial.









