글로벌 연구동향
핵의학
- [Korean J Radiol.] Diagnostic Performance of ¹⁸F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/CT for Chronic Empyema-Associated Malignancy.
성균관의대 / 천미주, 최준영*
- 출처
- Korean J Radiol.
- 등재일
- 2019 Aug
- 저널이슈번호
- 20(8):1293-1299. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.0843.
- 내용
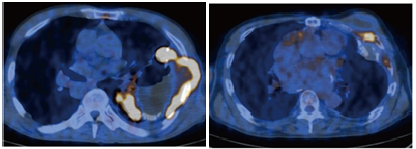
그림.1 FDG PET/CT로 만성 농흉 환자에서 암(왼쪽 사진) 또는 양성 염증(오른쪽 사진)으로 진단한 증례들.
Abstract
OBJECTIVE:
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the diagnostic performance of ¹⁸F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (¹⁸F-FDG PET/CT) for chronic empyema-associated malignancy (CEAM).MATERIALS AND METHODS:
We retrospectively reviewed the ¹⁸F-FDG PET/CT images of 33 patients with chronic empyema, and analyzed the following findings: 1) shape of the empyema cavity, 2) presence of fistula, 3) maximum standardized uptake value (SUV) of the empyema cavity, 4) uptake pattern of the empyema cavity, 5) presence of a protruding soft tissue mass within the empyema cavity, and 6) involvement of adjacent structures. Final diagnosis was determined based on histopathology or clinical follow-up for at least 6 months. The abovementioned findings were compared between the ¹⁸F-FDG PET/CT images of CEAM and chronic empyema. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was also performed.RESULTS:
Six lesions were histopathologically proven as malignant; there were three cases of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, two of squamous cell carcinoma, and one of poorly differentiated carcinoma. Maximum SUV within the empyema cavity (p < 0.001) presence of a protruding soft tissue mass (p = 0.002), and involvement of the adjacent structures (p < 0.001) were significantly different between the CEAM and chronic empyema images. The maximum SUV exhibited the highest diagnostic performance, with the highest specificity (96.3%, 26/27), positive predictive value (85.7%, 6/7), and accuracy (97.0%, 32/33) among all criteria. On ROC analysis, the area under the curve of maximum SUV was 0.994.CONCLUSION:
¹⁸F-FDG PET/CT can be useful for diagnosing CEAM in patients with chronic empyema. The maximum SUV within the empyema cavity is the most accurate ¹⁸F-FDG PET/CT diagnostic criterion for CEAM.
Author informationCheon M1, Yoo J1, Hyun SH2, Lee KS3, Kim H4, Kim J5, Zo JI5, Shim YM5, Choi JY6.
1
Department of Nuclear Medicine, Veterans Health Service Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
2
Department of Nuclear Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
3
Department of Radiology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
4
Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
5
Department of Thoracic Surgery and Cardiovascular Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
6
Department of Nuclear Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jynm.choi@samsung.com.
- 키워드
- Chronic empyema; Chronic empyema-associated malignancy; PET/CT; ¹⁸F-FDG
- 연구소개
- 만성 농흉은 암발생 위험도를 높이는 병 중의 하나인데, FDG PET/CT가 만성 농흉 환자에서 암 동방 여부를 감별하는 데 유용하다는 연구입니다.
- 덧글달기
- 이전글 [Sci Rep.] Predictive and Prognostic Value of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose Uptake Combined with Thymidylate Synthase Expression in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.
- 다음글 [BMC Cardiovasc Disord.] Effects of ezetimibe/simvastatin 10/10 mg versus Rosuvastatin 10 mg on carotid atherosclerotic plaque inflammation.









