글로벌 연구동향
핵의학
- 2018년 03월호
[J Nucl Med.] 64Cu-Labeled Repebody Molecules for Imaging of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Expressing Tumors.전남의대 / 표아영, 윤미선, 민정준*, 김동연*
- 출처
- J Nucl Med.
- 등재일
- 2018 Feb
- 저널이슈번호
- 59(2):340-346.
- 내용
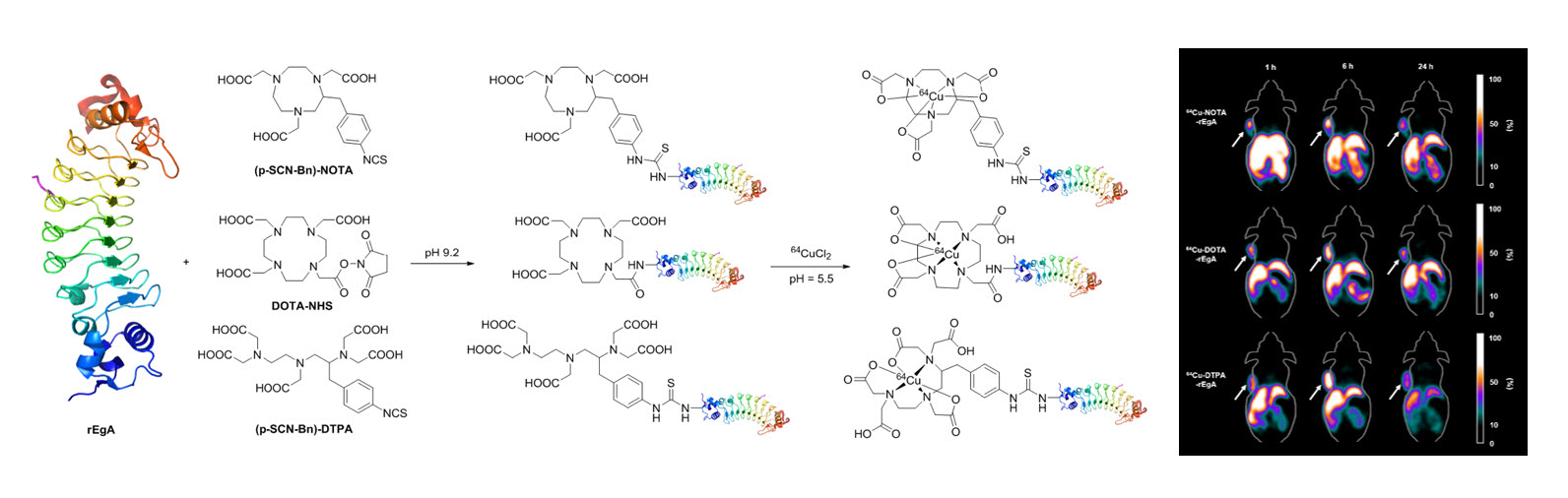
Abstract
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a member of the erbB family of receptors and is overexpressed in many tumor types. A repebody is a newly designed nonantibody protein scaffold for tumor targeting that contains leucine-rich repeat modules. In this study, 3 64Cu-labeled anti-EGFR repebodies with different chelators were synthesized, and their biologic characteristics were assessed in cultured cells and tumor-bearing mice. Methods: Repebodies were synthesized with the chelators 2-(p-isothiocyanatobenzyl)-1,4,7-triazacyclononane-N,N',N,″-triacetic acid trihydrochloride ([p-SCN-Bn]-NOTA), 2,2',2″-(10-(2-(2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yloxy)-2-oxoethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7-triyl) triacetic acid (DOTA-N-hydroxysuccinimide ester), or 1-(p-isothiocyanatobenzyl)diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid trihydrochloride ([p-SCN-Bn]-DTPA) in 1.0 M NaHCO3 buffer (pH 9.2) for 24 h. Purified NOTA-, DOTA-, and DTPA-conjugated repebody were radiolabeled with 64Cu in 0.1 M NH4OAc buffer (pH 5.5). To compare the EGFR-binding affinities of the repebodies, cellular uptake studies were performed with the human non-small cell lung cancer cell line H1650 (high expression of EGFR) and the human colon adenocarcinoma cell line SW620 (low expression of EGFR). Biodistribution and small-animal PET imaging studies were performed using H1650 tumor-bearing mice. Results: Radiochemical yields of the 64Cu-labeled repebodies were approximately 70%-80%. Cellular uptake of the NOTA-, DOTA-, and DTPA-repebodies was over 4-fold higher in H1650 cells than in SW620 cells at 1 h. The 3 repebodies had accumulated specifically in H1650 tumor-bearing nude mice by 1 h after intravenous injection and were retained for over 24 h, as measured by the percentage injected dose per gram of tissue (%ID/g). Tumor uptake of all repebodies increased from 1 to 6 h (at 1 h, 6.28, 8.46, and 6.91 %ID/g for NOTA-, DOTA-, and DTPA-repebody, respectively; at 6 h, 9.4, 8.28, and 10.1 %ID/g, respectively). H1650 tumors were clearly visible after injection of each repebody, with high tumor-to-background ratios (at 1 h, 3.43, 4.89, and 2.38 for NOTA-, DOTA-, and DTPA-repebody, respectively; at 6 h, 3.05, 4.36, and 2.08; at 24 h, 3.81, 4.58, and 2.86). Conclusion: The 3 64Cu-repebody complexes demonstrated specific and rapid uptake in EGFR-expressing tumorswithin 1 h and may have potential as novel EGFR imaging agents for PET.
Author information
Pyo A1,2, Yun M1,3, Kim HS1, Kim TY4, Lee JJ4, Kim JY5, Lee S2, Kwon SY1, Bom HS1, Kim HS4, Kim DY1, Min JJ6.
1 Department of Nuclear Medicine, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Hwasun, Korea.
2 Department of Chemistry, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea.
3 Chair for Biological Imaging, Technische Universitat München, Munich, Germany.
4 Department of Biological Sciences, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Daejeon, Korea; and.
5 Division of RI-Convergence Research, Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, Seoul, Korea.
6 Department of Nuclear Medicine, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Hwasun, Korea jjmin@jnu.ac.kr blueburr@gmail.com.
- 키워드
- 64Cu labeling; EGFR; molecular imaging; positron emission tomography; repebody
- 연구소개
- Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)을 표적할 수 있는 새로운 인공항체 리피바디(repebody)에 방사성동위원소 64Cu를 표지 하여 분자영상 프로브로써의 가능성 및 효율을 평가한 논문입니다. 리피바디는 기존 항체와 비교하였을 때, EGFR에 대한 비슷한 표적능을 가지지만 크기가 상대적으로 매우 작아 표적장기 외의 제거 속도가 월등히 뛰어난 장점을 가지고 있습니다. 따라서 64Cu 표지 리피바디를 이용하여 영상의 질이 우수한 PET영상 획득이 가능하였으며 이의 분석을 통해 종양의 EGFR 발현 정도를 정량할 수 있었습니다. 또한 리피바디의 생물학적 특징은 구조가 다른 리간드를 사용하여 64Cu를 표지하였을 때도 유지됨을 확인 할 수 있었습니다. 이러한 영상기술의 개발은 조직 채취가 없이 특정 암의 치료표적 발현 유무를 평가할 수 있기 때문에 차후 동반진단기술에도 이용될 수 있을 것으로 생각됩니다.
- 덧글달기








편집위원
CU-64 anti-EGFR repeboby로 EFGR발현 종양을 영상화 할 수 있음을 보여준 핵의학 분자영상연구로 향후 표적치료에 핵의학영상기술의 적용범위를 넓힐 수 있는 중요한 연구임. 종양관련 의사와 임상 핵의학자의 관심을 끌 논문으로 생각되며 또한 분자영상기초연구자에게 큰 영향을 미칠 수 있는 연구임.
덧글달기닫기2018-03-15 15:17:32
등록
편집위원2
최근 Cu-64 이용한 theranostics 기사가 원자력의학원에서도 있었고, 새로운 tracer들의 임상적용에의 도전 및 적용은 우리 핵의학 분야에 의미있는 부분이라 생각합니다.
덧글달기닫기2018-03-15 15:36:29
등록