글로벌 연구동향
방사선종양학
- [Br J Radiol.] Results of re-irradiation for pelvic recurrence in anorectal cancer patients.
서울의대 / 박영희, 김규보, 지의규*
- 출처
- Br J Radiol.
- 등재일
- 2019 May
- 저널이슈번호
- 92(1097):20180794. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20180794. Epub 2019 Mar 29
- 내용
Abstract
OBJECTIVE:
To evaluate outcomes and toxicity profiles after re-irradiation in patients with pelvic recurrence of anorectal cancer.METHODS:
25 anorectal cancer patients who received re-irradiation for pelvic recurrence between 2005 and 2015 were included. For initial treatment, all patients underwent surgical resection and preoperative or postoperative radiotherapy.RESULTS:
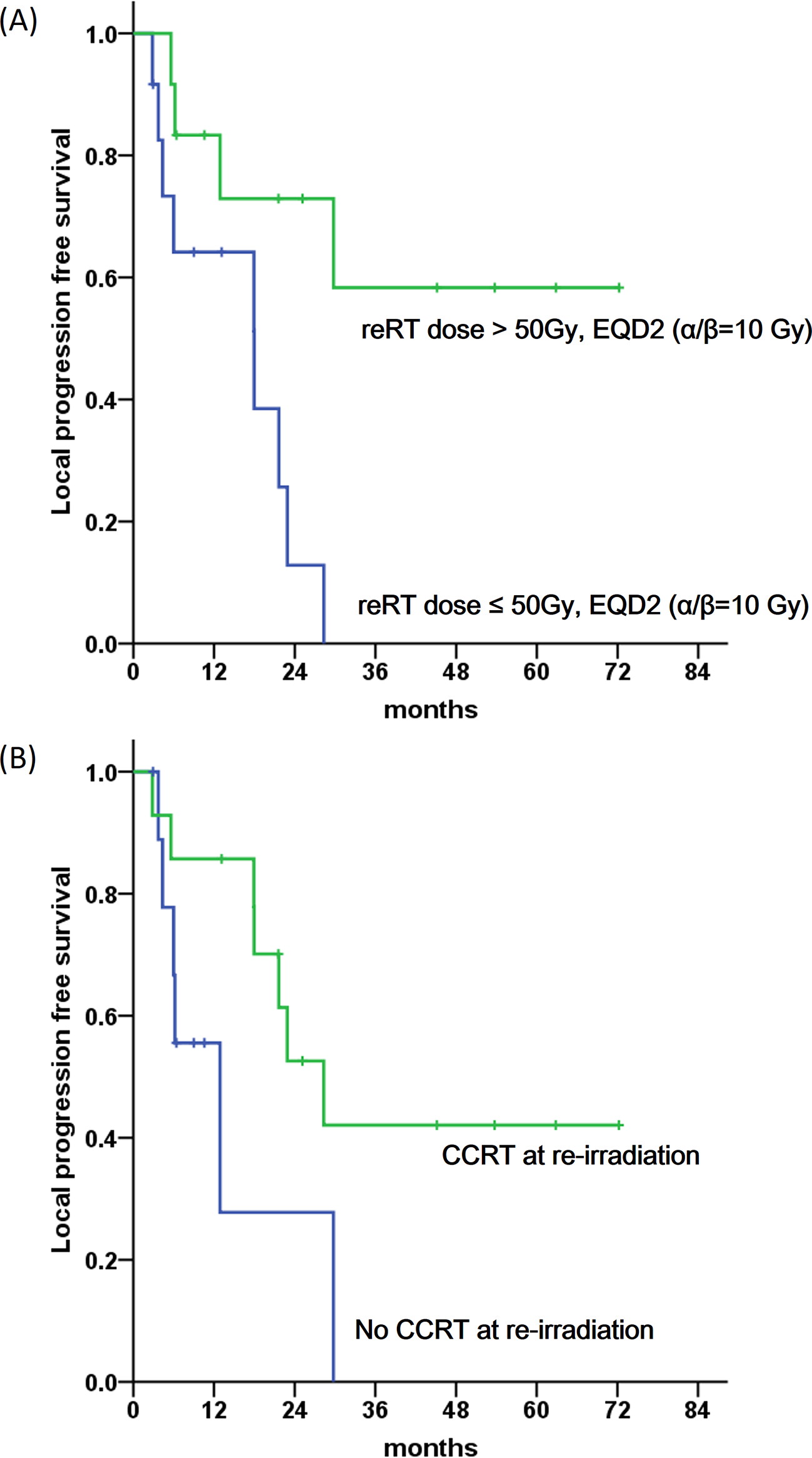
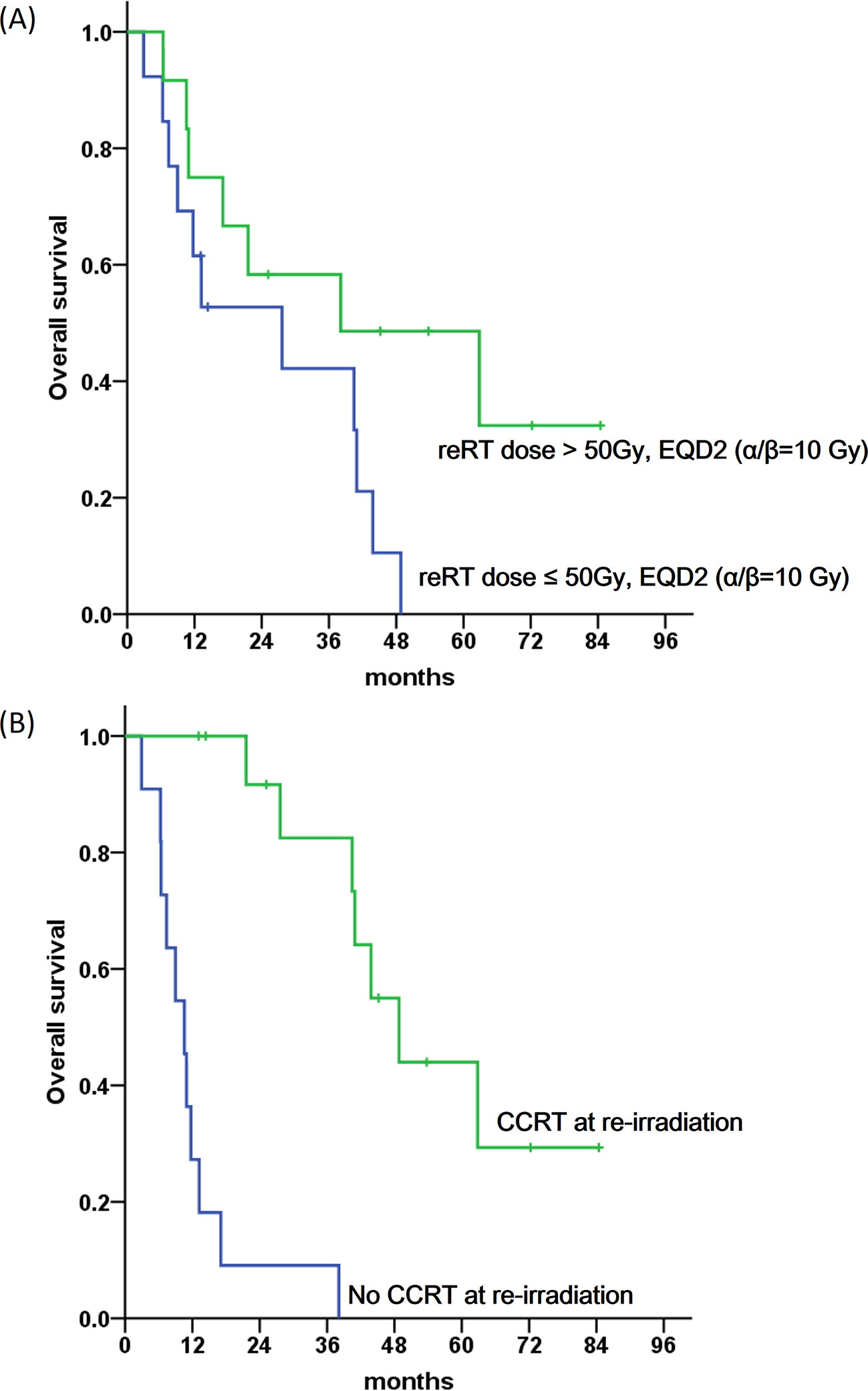
The median follow-up duration was 21.5 months (range, 2.9-84.4). After a median of 43.3 months (range, 11.7-218.5), patients received re-irradiation with a median dose of 45 Gy (range, 36-60). The equivalent dose in 2 Gy fractions (EQD2) of re-irradiation-calculated using α/β = 10 Gy-ranged from 34.5 to 84.0 Gy (median, 46.4). Surgical resection was performed for 11 patients, and 14 patients received concurrent chemotherapy with re-irradiation. The 3-year local progression-free survival was 29.7%. The 3-year overall survival was 49.7%. Concurrent chemotherapy with re-irradiation and re-irradiation doses >50 Gy EQD2α/β=10 were significant prognostic factors for local progression free survival and overall survival according to multivariate analysis. 90% (9 of 10) of patients with symptoms had improvement after re-irradiation. Among 23 patients available for evaluation of late toxicity, 12 developed late toxicities. There were no Grade 4 late toxicities, and 6 patients had Grade 3 late toxicities (small bowel obstruction, bowel perforation and fistula).CONCLUSION:
Re-irradiation for pelvic recurrence of anorectal cancer improved symptoms of patients but the rate of late toxicity was high. Further investigation for patient selection is required.ADVANCES IN KNOWLEDGE:
Re-irradiation could be considered as a possible option for pelvic recurrence of anorectal cancer in selected patients.
Author informationPark Y1, Kim K2, Park HJ3, Jeong SY4, Park KJ4, Han SW5, Kim TY5, Chie EK6.
1
1 Department of Radiation Oncology, Soonchunhyang University Seoul Hospital , Seoul , Republic of Korea.
2
2 Department of Radiation Oncology, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine , Republic of Korea.
3
3 Department of Radiation Oncology, Hanyang University College of Medicine , Seoul, Republic of Korea.
4
4 Department of Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine , Seoul , Republic of Korea.
5
5 Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine , Seoul , Republic of Korea.
6
6 Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University College of Medicine , Seoul , Republic of Korea.
- 연구소개
- 항문직장암의 재발에 대해 방사선 재치료를 시행한 25명의 환자들의 치료 결과를 분석한 단일기관 연구입니다. 항암화학요법과의 병행 치료와 50Gy 이상의 고선량 치료가 국소제어 및 전체생존율에 유의한 예후인자였습니다. 증상이 동반된 환자중 90%에서 증상이 개선되었고, 4도 이상의 부작용은 없었으나, 3년 3도 부작용 발생율이 52.5%로 환자 적용에 주의가 필요함을 확인하였습니다.
- 덧글달기
- 이전글 [Cancers (Basel).] Clinical Significance of Lymph-Node Ratio in Determining Supraclavicular Lymph-Node Radiation Therapy in pN1 Breast Cancer Patients Who Received Breast-Conserving Treatment (KROG 14-18): A Multicenter Study.
- 다음글 [In Vivo.] Combined Chemoradiotherapy-induced Weight Loss Decreases Survival in Locally Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients.










편집위원
제한된 숫자의 환자이기는 하나, 직장암에서 재방사선치료의 부작용 및 치료결과를 분석하여 제시함.
2019-06-17 11:12:36
편집위원
진단 및 치료방법의 발전으로 생존율이 증가하면서 re_RT가 의뢰되는 증례가 많아졌는데, 본 연구결과를 참고로 re_RT 후의 높은 Gr3 치료독성을 고려하여 주의깊게 적용해야 하겠습니다.
2019-06-24 13:44:27
편집위원3
최근 종양치료 성적향상과 암환자 생존기간의 연장으로 재방사선치료의 빈도와 중요성이 증가하는 상황에서 환자 선택의 기준과 재방사선량의 설정은 어렵고도 중요한 관심사항이다.
2019-06-24 13:46:27