글로벌 연구동향
방사선종양학
- [J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol.] Generation of virtual lung single-photon emission computed tomography/CT fusion images for functional avoidance radiotherapy planning using machine learning algorithms.
서울특별시보라매병원 / 장범섭, 장지현*
- 출처
- J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol.
- 등재일
- 2019 Apr
- 저널이슈번호
- 63(2):229-235. doi: 10.1111/1754-9485.12868. Epub 2019 Mar 15.
- 내용
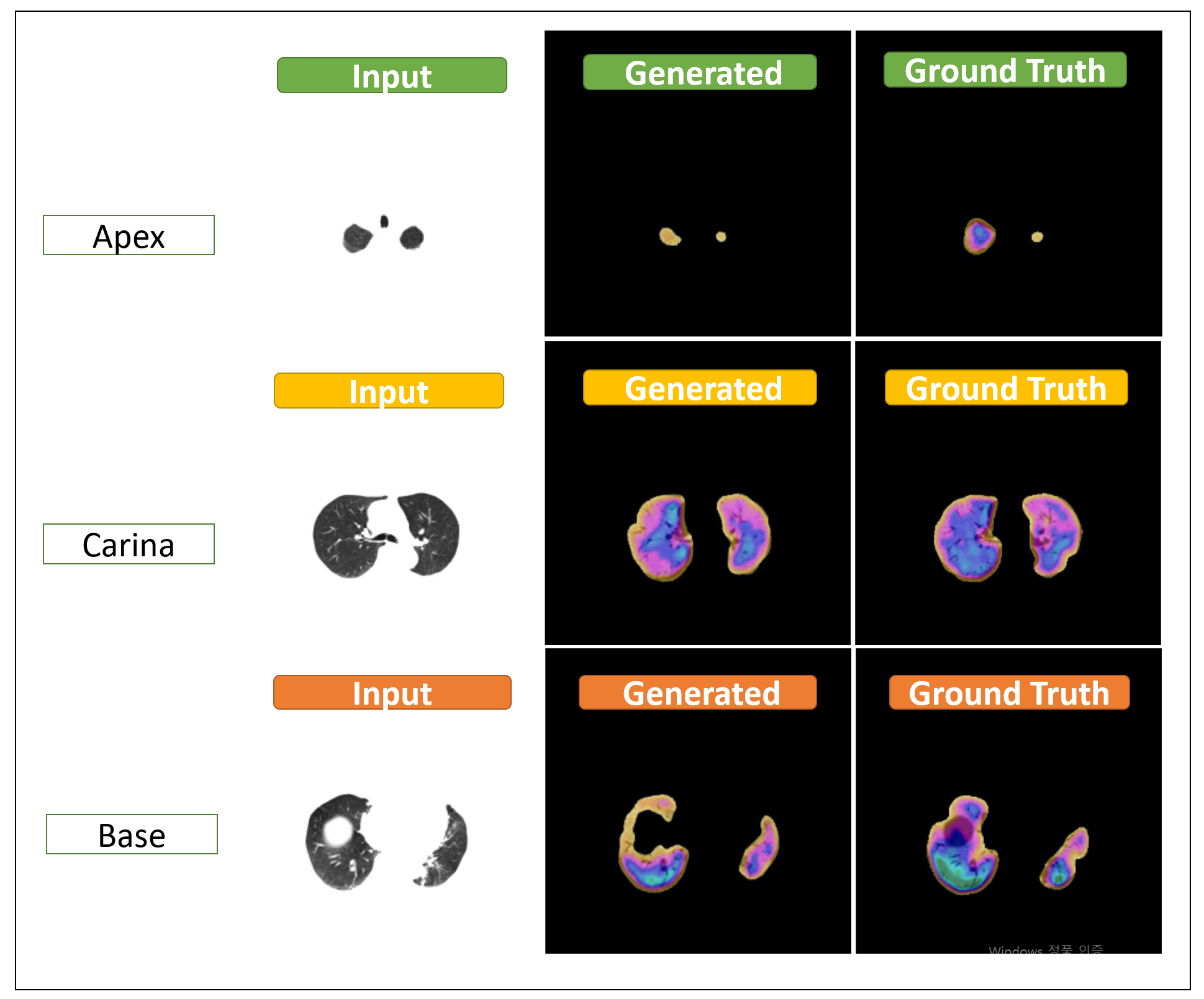
Abstract
INTRODUCTION:
Functional image-guided radiotherapy (RT) planning for normal lung avoidance has recently been introduced. Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)/CT can help identify the functional areas of lungs, but it is associated with delayed treatment time, additional costs and unexpected radiation exposure. In this study, we propose a machine learning algorithm that can generate functional chest CT images using the conditional generative adversarial networks (cGANs).METHODS:
We collected a total of 54 lung perfusion SPECT/CT image sets from lung cancer patients who had been treated at a single institution. CT-to-SPECT image pairs that contained no lung voxels or did not match anatomically (on account of the patient's breathing) were removed at the physician's discretion. After we excluded the inappropriate images, we selected 3054 CT-to-SPECT image pairs as the training set (49 patients) and the 400 testing sets (five patients). The model was trained using the cGAN algorithm.RESULTS:
We firstly evaluated the model based on multiscale SSIM (MS-SSIM). With the 400 image pairs of the testing set, we obtained a lung SPECT/CT fusion image for which the MS-SSIM was 0.87 (0.60-0.99) compared with the original image. We next estimated a gamma index between the generated and the ground truth images, resulting in a mean passing rate of 97.7 ± 1.2% with a 2%/2 mm threshold. These results supported the potential to generate functional areas of the lung parenchyma directly from chest CT images using the machine learning algorithm.CONCLUSION:
The results indicate that the cGAN model used here can generate functional areas from RT planning chest CT images. This could be used for functional image-guided RT planning, for example, to spare patients' lung function without additional imaging modalities and costs. Additional studies are needed with many more training and test sets.
Author informationJang BS1, Chang JH2, Park AJ3, Wu HG1.
1
Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
2
Department of Radiation Oncology, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
3
Artificial Intelligence Research and Development Laboratory, SELVAS AI Incorporation, Seoul, Korea.
- 키워드
- SPECT ; adversarial network; functional radiotherapy; lung cancer; machine learning
- 연구소개
- 폐암 환자의 방사선치료로 유발될 수 있는 폐 손상을 줄이기 위해서 최근 functional image를 고려하여 치료 계획을 시도하는 경향이 생겨나고 있습니다. 폐암 환자들은 흡연력이나 기저질환 등으로 폐의 기능이 떨어져 있는 경우가 많기 때문에, 폐기능이 확연히 저하되어있는 부분을 파악할 수 있다면 방사선치료 계획에 큰 도움이 될 수 있습니다. 그러나 현실적으로 모든 폐암 환자에서 SPECT/CT 등의 3D functional image를 얻는 것은, 경제적으로도, 방사선에 대한 노출 측면에서도 제한점이 있습니다. 본 연구에서는 SPECT/CT image 자체를 딥러닝을 이용한 기계학습을 학습시켜서 방사선 치료 계획용 CT 이미지에서 환자의 방사선 치료 자세와 기구를 유지한 채 SPECT/CT fusion 유사 이미지를 생성하는데 적용을 하였고, 결론적으로 CT 영상을 통해 실제 SPECT/CT 이미지와 유사도가 높은 이미지를 얻을 수 있었습니다. 아직은 연구 초기 단계이고 validation을 계획 중에 있는 개념이지만, 추후 해당 기술을 적용할 수 있게 된다면, 상대적으로 기능이 활성화되어있는 부분에 방사선이 조사되는 것을 가급적으로 피하고 폐기능이 저하되어 있는 부분에 조사되도록 하여 방사선 치료로 인한 폐 손상을 최소화 시키는 방사선치료 계획이 가능해질 것입니다. 또한 향후 이러한 알고리즘을 다른 장기에 대해서도 확장한다면, functional image-guided 방사선치료를 여러 암환자에게 적용하는데 도움을 줄 수 있을 것이라 생각합니다.
- 덧글달기
- 이전글 [PLoS One.] Stereotactic body radiation therapy for locally advanced pancreatic cancer.
- 다음글 [Radiother Oncol.] Significance of perineural and lymphovascular invasion in locally advanced rectal cancer treated by preoperative chemoradiotherapy and radical surgery: Can perineural invasion be an indication of adjuvant chemotherapy?









