글로벌 연구동향
방사선종양학
 Verification of Accuracy of CyberKnife Tumor-tracking Radiation Therapy Using Patient-specific Lung Phantoms.
Verification of Accuracy of CyberKnife Tumor-tracking Radiation Therapy Using Patient-specific Lung Phantoms.(울산의대/정진홍, 송시열*)
- 출처
- Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys
- 등재일
- 2015 Jul 15
- 저널이슈번호
- 92(4):745-53
- 내용

[Abstract]PURPOSE:
To investigate the accuracy of the CyberKnife Xsight Lung Tracking System (XLTS) compared with that of a fiducial-based target tracking system (FTTS) using patient-specific lung phantoms.
METHODS AND MATERIALS:
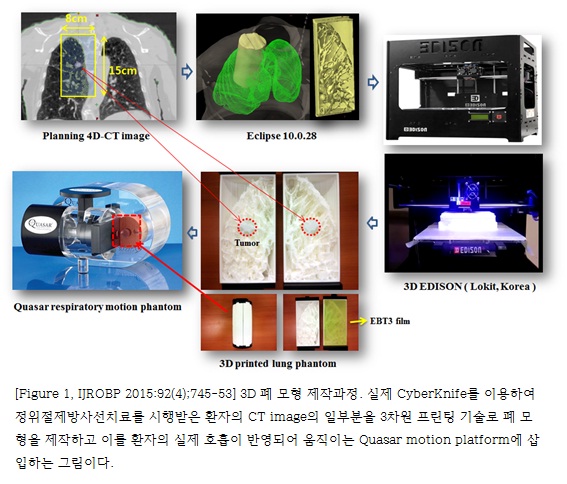
Three-dimensional printing technology was used to make individualized lung phantoms that closely mimicked the lung anatomy of actual patients. Based on planning computed tomographic data from 6 lung cancer patients who underwent stereotactic ablative radiation therapy using the CyberKnife, the volume above a certain Hounsfield unit (HU) was assigned as the structure to be filled uniformly with polylactic acid material by a 3-dimensional printer (3D Edison, Lokit, Korea). We evaluated the discrepancies between the measured and modeled target positions, representing the total tracking error, using 3 log files that were generated during each treatment for both the FTTS and the XLTS. We also analyzed the γ index between the film dose measured under the FTTS and XLTS.
RESULTS:
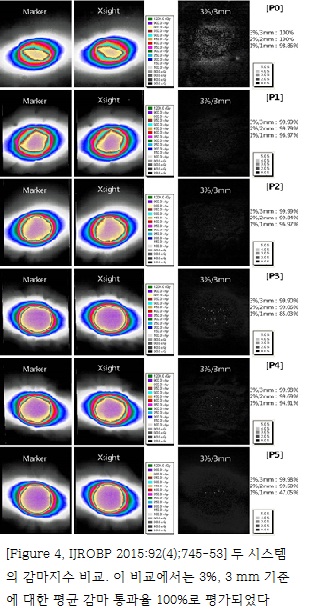
The overall mean values and standard deviations of total tracking errors for the FTTS were 0.36 ± 0.39 mm, 0.15 ± 0.64 mm, and 0.15 ± 0.62 mm for the craniocaudal (CC), left-right (LR), and anteroposterior (AP) components, respectively. Those for the XLTS were 0.38 ± 0.54 mm, 0.13 ± 0.18 mm, and 0.14 ± 0.37 mm for the CC, LR, and AP components, respectively. The average of γ passing rates was 100% for the criteria of 3%, 3 mm; 99.6% for the criteria of 2%, 2 mm; and 86.8% for the criteria of 1%, 1 mm.
CONCLUSIONS:
The XLTS has segmentation accuracy comparable with that of the FTTS and small total tracking errors.
[Author information]
Jung J1, Song SY2, Yoon SM3, Kwak J3, Yoon K3, Choi W4, Jeong SY5, Choi EK3, Cho B3.
1Department of Radiation Oncology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea; Department of Radiation Oncology, Kyung Hee University Medical Center, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
2Department of Radiation Oncology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea. Electronic address: coocoori@gmail.com.
3Department of Radiation Oncology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
4Department of Radiation Oncology, Gangneung Asan Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung, Republic of Korea.
5Asan Institute for Life Science, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
- 연구소개
- 폐암은 전 세계적으로 높은 사망률을 보이는 암이지만, 초기 폐암의 경우에는 일반적으로 수술적 절제를 통해 완치를 기대해 볼 수 있다. 하지만 수술을 받지 못할 만한 기저질환을 가지고 있거나 폐기능이 나쁜 수술이 불가능한 초기폐암에서는 지난 십수년 동안 정위절제방사선치료 (Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy, SABR)가 대안으로 부상하여 수술에 뒤떨어지지 않는 좋은 치료성적을 보여주고 있다. 적은 양의 방사선을 수십 회 조사하는 기존의 일반적인 방사선치료기법과는 달리 정위절제방사선치료는 한 번에 많은 양의 방사선을 집중 조사하는 기법으로 종양을 정확하게 조준할 수 있는 기술이 매우 중요하다. 특히 호흡에 따라 위아래로 크게 움직이는 폐나 간에 이를 시행하려면 호흡 자체를 제어하거나 종양의 위치를 실시간으로 측정할 수 있는 기술이 있어야 한다. 본 연구에서 그 정확도를 측정하고자 했던 CyberKnife는 직교 X선 영상을 이용하여 실시간 종양의 움직임을 추적할 수 있는 대표적인 장비로서 추적의 정확성을 위하여는 표지자 (marker)의 삽입이 필수적이었다. 하지만 대부분 폐기능이 좋지 않은 환자임을 고려할 때 표지자 삽입으로 인한 기흉, 출혈 등 치료를 늦추는 부작용의 발생 위험성이 있어 최근에는 표지자 삽입 없이 종양 그 자체를 추적하는 ’Xsight lung 추적 시스템‘이 개발되어 사용되기 시작하였다. 하지만 이러한 무표지자 종양추적 시스템의 정확성과 안정성에 대하여는 많은 연구가 이루어지지는 않았다. 본 연구에서 저자들은 ‘표지자 기반 표적추적 시스템과 비교하여 ’Xsight lung 추적 시스템‘의 정확도를 검증하고자 하였는데, 기존의 사용되는 폐 모형은 ’Xsight lung 추적 시스템‘에서 종양이 관찰되지 않기 때문에, 3차원 프린팅 기술로 실제 환자의 폐와 동일한 모양의 폐 모형을 제작한 것이 참신한 발상이자 이 연구를 가능하게 했던 가장 중요한 부분이었다. 실험 결과 표지자 기반 표적 추적 시스템의 전체 추적 오차의 평균과 표준편차는 두미 축, 좌우 축, 그리고 전후 축으로 각각 0.36 ± 0.39 mm, 0.15 ± 0.64 mm, 그리고 0.15 ± 0.62 mm 이었다. ’Xsight Lung 추적 시스템‘에 대해서는 두미 축, 좌우 축, 그리고 전후 축으로의 평균과 표준편차가 각각 0.38 ± 0.54 mm, 0.13 ± 0.18 mm, 그리고 0.14 ± 0.37 mm 이었다. 두 시스템의 감마지수 비교에서는 3%, 3 mm 기준에 대한 평균 감마 통과율 100%, 2%, 2 mm 기준에 대한 평균 감마 통과율 99.6%, 그리고 1%, 2 mm 기준에 대한 평균 감마 통과율 86.8%로 평가되었다. 결론적으로 ’Xsight Lung 추적 시스템‘이 ’표지자 기반 표적추적 시스템‘과 대등한 구분 정확도를 가진다고 검증하였다.
- 덧글달기
- 이전글 Does internal mammary node irradiation affect treatment outcome in clinical stage II-III breast cancer patients receiving neoadjuv ant chemotherapy?
- 다음글 A multicenter analysis of adjuvant therapy after surgery for stage IIIC endometrial adenocarcinoma: A Korean Radiation Oncology Group study (KROG 13-17).









